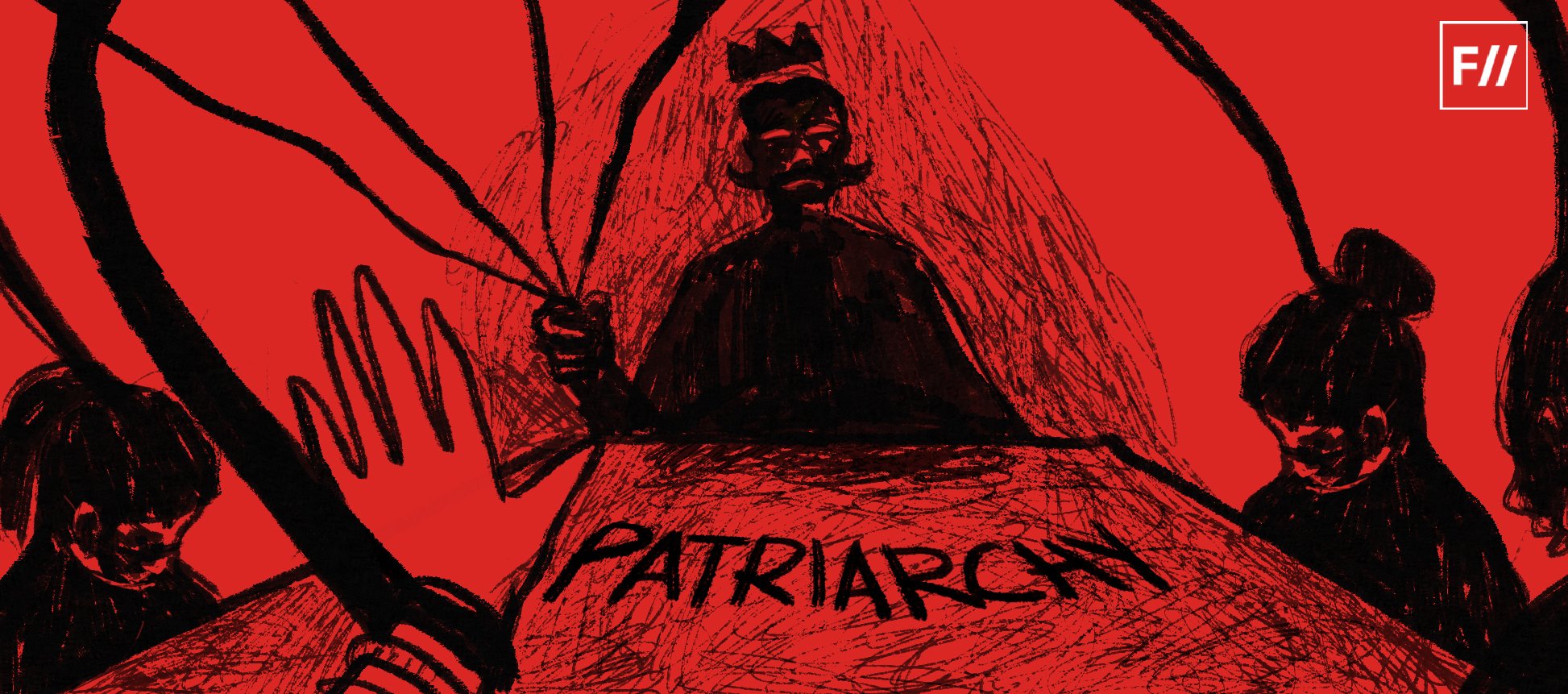
Patriarchy is characterised by a hierarchal system in which men get more access to resources and opportunities and is manifested through social, religious, legal, and political institutions.
Patriarchy is an institutionalised social system that endorses the authority and dominance of men over women. Etymologically speaking, the term has its roots in the Greek word patriarkhes, which means the rule of the father. The concept of patriarchy has a complex history. It originates from ancient religious texts, origin stories, and cultural customs.
The most revered religious texts or the divine commandments reinforce a belief that men are superior to women. This religious and cultural authority further aids in the propagation of patriarchal ideology leading to the disempowerment of women. Throughout history, these beliefs have evolved and have acquired a firm hold over the way people are socialised. This social construction of gender norms leads to the blind acceptance of patriarchal systems among men as well as women, in almost all societies.
Major approaches
A leading theorist of patriarchy Sylvia Walby, defines patriarchy as “a system of social structures and practices in which men dominate, oppress, and exploit women.” It is characterised by a hierarchal system in which men get more access to resources and opportunities and is manifested through social, religious, legal, and political institutions. An anthropological perspective best describes patriarchy as a broader structure of social hierarchy within a family, where the eldest male holds the position of authority.
The patriarchal ideology perpetuates gender inequality and justifies it by highlighting the biological differences between males and females. While sociobiologists like Steven Goldberg believe that genetic and reproductive factors are responsible for gender inequality, sociologists completely reject this justification by emphasising the role of the social construction of gender or the process of socialisation in reinforcing patriarchy.
Feminist thinkers on patriarchy
Feminist thinkers have had extensive discussions about patriarchy, often depicting it as a key factor in the oppression of women. According to radical-libertarian feminist thinker, Shulamith Firestone, patriarchy is the outcome of the biological differences between men and women, specifically women’s reproductive functions. Gerda Lerner, a feminist historian, argues that the control men have over women’s sexual and reproductive processes is both a root cause and a result of patriarchy.

According to Alison Jaggar, patriarchy is the main reason why women are oppressed, and she emphasises how it contributes to women feeling disconnected from their bodies. These thinkers, therefore uphold the beliefs propounded by the Sociobiologists.
Besides these radical feminist thinkers, theorists such as Iris Marion Young and Heidi Hartmann argue that patriarchy, along with other systems like capitalism, contributes to the creation and continuation of the oppression of women. They use Marxist phrases like “patriarchal capitalism” or “capitalist patriarchy” to describe this interdependent and interactive relationship.
Myriad manifestations of patriarchy
One way in which patriarchy is manifested in various aspects of society is through the tradition of passing down family names only through males. Another way is the lower chances women have of getting promoted in professional environments.
Women and girls often have limited educational opportunities because of societal attitudes and gender norms that favour men. Within the family system, there is a social structure that favours male children over female children in terms of their participation in education. Factors like caste, ethnicity, and socioeconomic background make the educational marginalisation of female students worse.
Discriminatory practices against girls’ education continue to exist due to patriarchal beliefs, which are held by both male and female parents. This shows how deeply ingrained and long-standing patriarchal traditions can be in a culture. Women face various forms of oppression and societal expectations related to gender within their own homes. The concept of the “wall of patriarchy” refers to the barriers that prevent women from fully exercising their decision-making authority within the household, thus hindering their empowerment. These factors can greatly impact their career goals and perspectives.
People who directly experience private patriarchy are more likely to value authenticity in their professional endeavours. On the other hand, those who witness it indirectly through their mothers’ experiences tend to gravitate towards jobs that involve challenging societal norms.
Discriminatory practices
One of the main reasons why women face obstacles in accessing education and employment is because of patriarchal structures that exist in both households and politics. These structures are further strengthened by socio-economic difficulties and a lack of parental education. The statement highlights how patriarchy has a profound and extensive impact on women’s empowerment.
People who criticise patriarchy argue that it not only oppresses women but also men. Men are often taught to follow strict gender roles, which can lead to suppressing their emotions and making them more vulnerable to abuse. For example, society often expects men to hide their emotions and not show vulnerability. Unfortunately, this can lead to higher rates of depression and suicide among men.
Women in India also face significant challenges in areas such as healthcare, decision-making, financial independence, and education. The presence of gender bias in domestic tasks as well as at workplaces worsens these challenges, which in turn contributes to all the issues related to patriarchy.
About the author(s)
Insha Qayoom Shah is a Research Scholar from the Department of English, University of Kashmir pursuing her PhD on Female Revisionary Mythmaking: A Study of Select Novels. The areas of her interest include Feminism, Mythology and the Revisionary literature. She has presented four papers in different national and international conferences. She has also contributed chapters in three books dealing with the feminism and gender studies.