Today on the World Sexual Health Day, Feminism In India along with Find My Method, are giving you a crash course on the various methods of contraception. Yes, there exists more than two, three or even four methods of contraception. And with so many methods available, how do you decide which one suits you best? Which is why Find My Method helps you find as well as compare the contraceptive method for you. Visit Find My Method right now to find the perfect contraceptive method for you!
What is Contraception?
Contraception refers to any device or method used to prevent pregnancy. It is also often called birth control or fertility control. Some contraceptive methods, namely condoms, can also help prevent sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Various Contraceptive Methods, Explained!
There are various contraceptive methods that one can choose. Let’s take a look at take these methods!
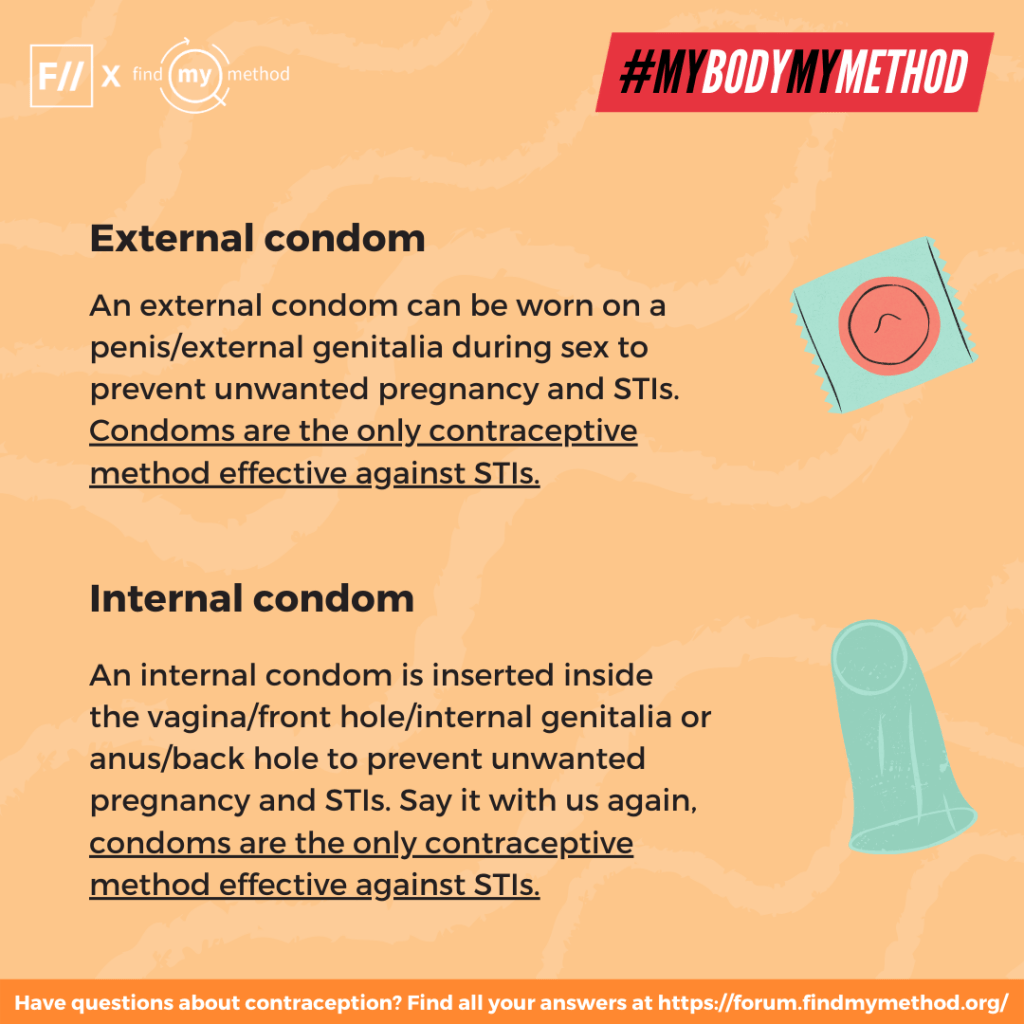
1. External condoms: An external condom can be worn on a penis/external genitalia during sex to prevent unwanted pregnancy and STIs. Condoms are the only contraceptive method effective against STIs. Find more about external condoms here.
2. Internal condoms: An internal condom is inserted inside the vagina/front hole/internal genitalia or anus/back hole to prevent unwanted pregnancy and STIs. Say it with us again, condoms are the only contraceptive method effective against STIs. Find more about internal condoms here.
Also read: A Western Feminist History Of Oral Contraception
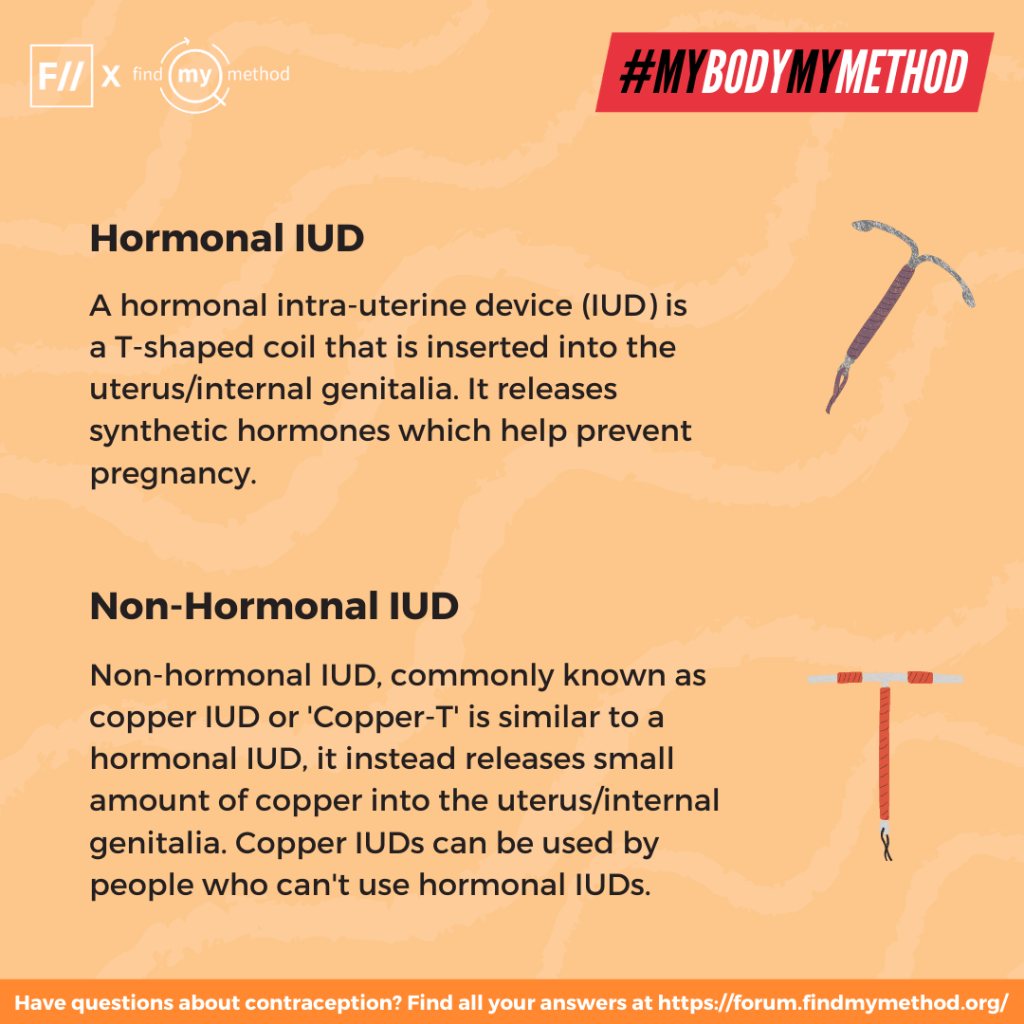
3. Hormonal intra-uterine device (IUD): A hormonal intra-uterine device (IUD) is a T-shaped coil that is inserted into the uterus/internal genitalia. It releases synthetic hormones which help prevent pregnancy. Find more about hormonal IUDs here.
4. Non-hormonal intra-uterine device (IUD): Non-hormonal IUD, commonly known as copper IUD or ‘Copper-T’ is similar to a hormonal IUD, it instead releases small amount of copper into the uterus/internal genitalia. Copper IUDs can be used by people who can’t use hormonal IUDs. Find more about non-hormonal IUDs here.
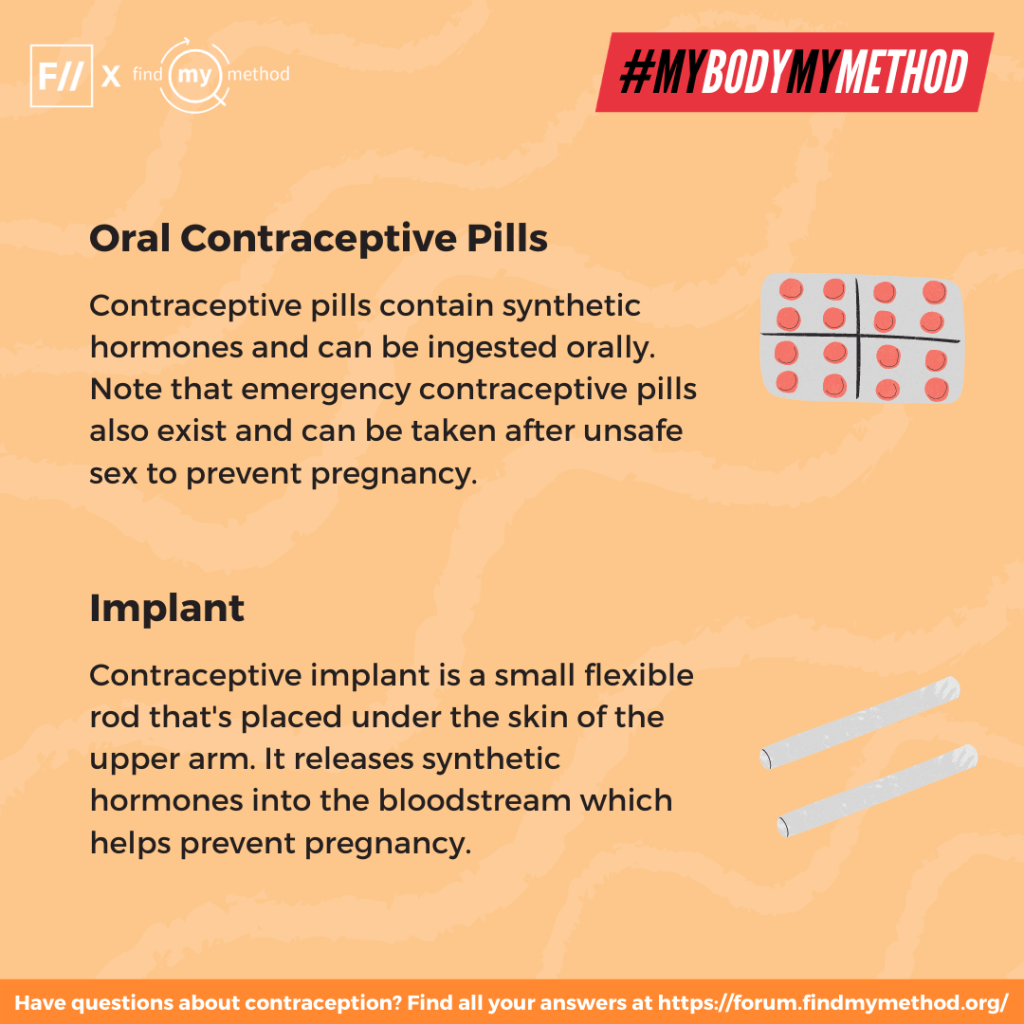
5. Oral contraceptive pills: Contraceptive pills contain synthetic hormones and can be ingested orally. Note that emergency contraceptive pills also exist and can be taken after unsafe sex to prevent pregnancy. Find more about oral contraceptive pills here.
6. Implant: Contraceptive implant is a small flexible rod that’s placed under the skin of the upper arm. It releases synthetic hormones into the bloodstream which helps prevent pregnancy. Find more about the implant here.
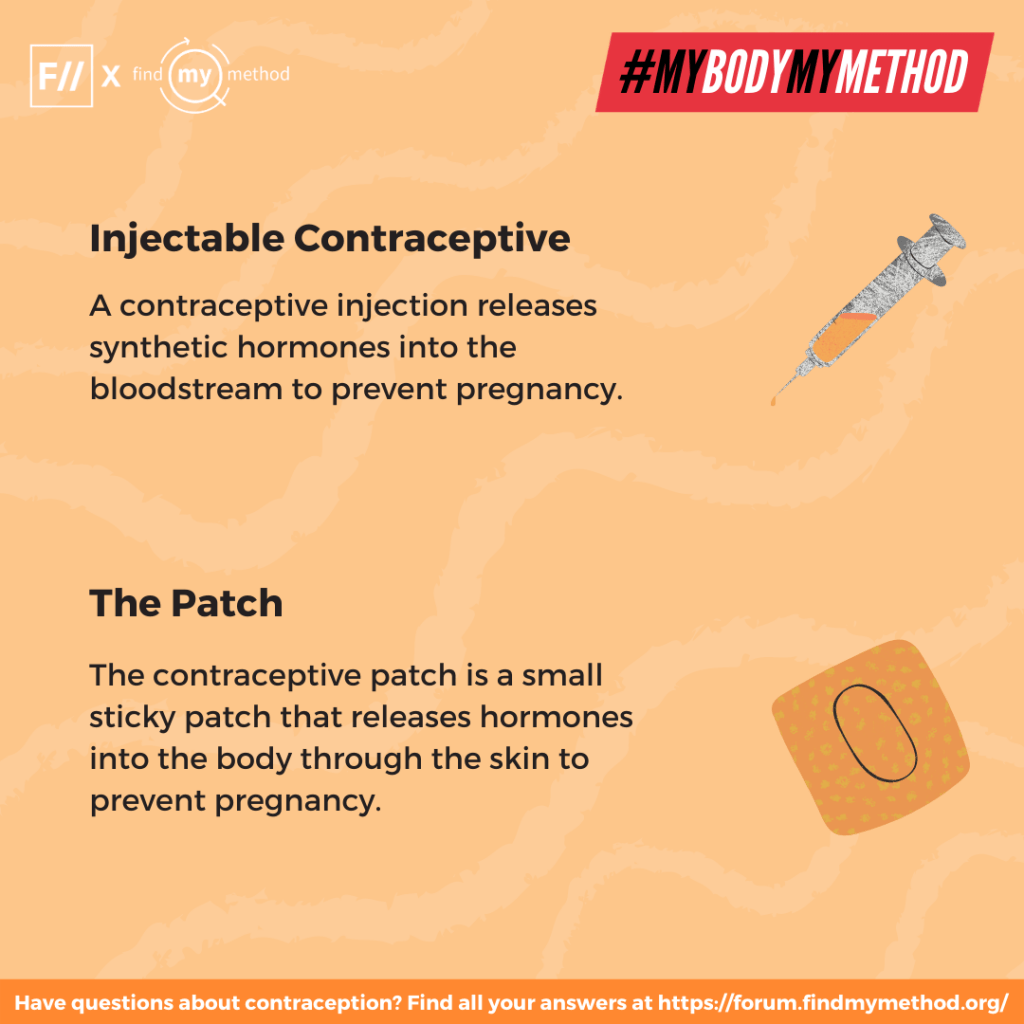
7. Injectable contraceptive: A contraceptive injection releases synthetic hormones into the bloodstream to prevent pregnancy. Find more about the injectable contraceptive here.
8. The Patch: The contraceptive patch is a small sticky patch that releases hormones into the body through the skin to prevent pregnancy. Find more about the patch here.
9. Cervical cap: A cervical cap is a circular dome made of thin, soft silicone that’s inserted into the vagina/front hole. It covers the cervix and prevents the entry of sperm into the uterus/internal genitalia. Find more about cervical cap here.
10. Spermicide: Spermicide is a contraceptive substance which contains chemicals that destroy sperms. It is inserted into the vagina/front hole and can be used alone or with other barrier methods such as cervical cap, condoms or diaphragm. Find more about spermicides here.
11. Sponge : The contraceptive sponge is a small, round sponge made from soft plastic. It is inserted vaginally/into the front hole prior to sex. It contains spermicide which helps prevent pregnancy. Find more about the sponge here.
12. Diaphragm: Diaphragms are similar to cervical caps. It covers the cervix during sex which helps prevent pregnancy. For a diaphragm to work best, it must be used with spermicide. Find more about diaphragm here.
Also read: Contraception Beyond Condoms: The Many Kinds Of Birth Control
13. The Ring: The ring is a small soft, plastic ring that is inserted into the vagina/front hole. It releases a continuous dose of hormones into the bloodstream to prevent pregnancy. Find more about the ring here.
14. Sterilisation: Surgical processes such as tubectomy (blocking fallopian tubes) and vasectomy (blocking sperm to reach semen) can also help prevent pregnancy. Find more about sterilisation here.
15. Withdrawal: The withdrawal method, also known as ‘pull out’ method involves pulling out just before ejaculation. Withdrawal is only efficient when used with another contraceptive method, eg. condoms. Find more about the withdrawal method here.
16. Abstinence: Abstaining from sex can also be a contraceptive method. People can abstain from sex for many reasons such as not wanting to have sex at all or waiting to have sex. Find more about abstinence here.
Do you have questions about sex, pleasure or birth control? On Find My Method’s newly launched forum, you can discuss all your questions and concerns about contraception and remain anonymous. With a room for discussion dedicated to users from India, you can ask and share localised information both in English and Hindi. Click here to visit the forum right now.
This article is published as a part of the #MyBodyMyMethod awareness campaign on contraception. Feminism in India and Find My Method will be talking about the various forms of contraception, busting contraception myths and taboo, and much more throughout the month of September, 2020. Find My Method works to provide accurate contraceptive information for a global audience. You can find localised information that is easy to understand, and is globally representative on Find My Method’s website and forum. You can follow them on Twitter, Facebook and Instagram.
About the author(s)
Feminism In India is an award-winning digital intersectional feminist media organisation to learn, educate and develop a feminist sensibility and unravel the F-word among the youth in India.