Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the cervix – which is the entrance to the uterus from the vagina. About 99% of cases of cervical cancer are linked to infection with high-risk human papillomaviruses (HPV). This virus is also the most common cause of STIs. It is transmitted through sexual contact that can include intimate skin-to-skin contact, vaginal–penile penetration, anal sex, oral sex and the use of sex toys or other objects.
But the good news is that it can be prevented! The HPV vaccine can protect an individual against human papillomavirus strains that cause cervical cancer and has proved to cut the risk of getting it by 90%.
What Is The HPV Vaccine?
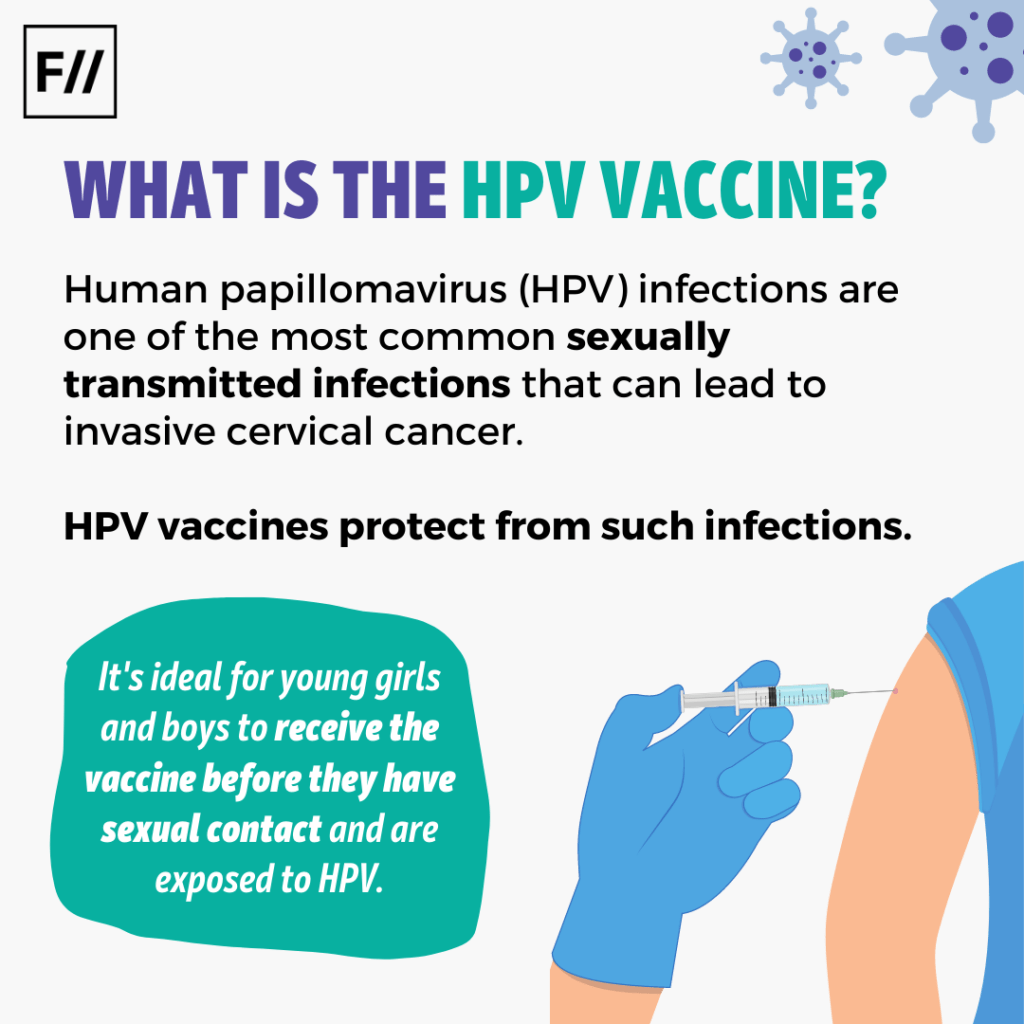
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infections are one of the most common sexually transmitted infections that can lead to invasive cervical cancer. HPV vaccines protect from such infections.
Since HPV is transmitted via sexual contact, it is ideal to receive the vaccine at a young age, before they have sexual contact and are exposed to the virus.
Who Should Get The HPV Vaccine?
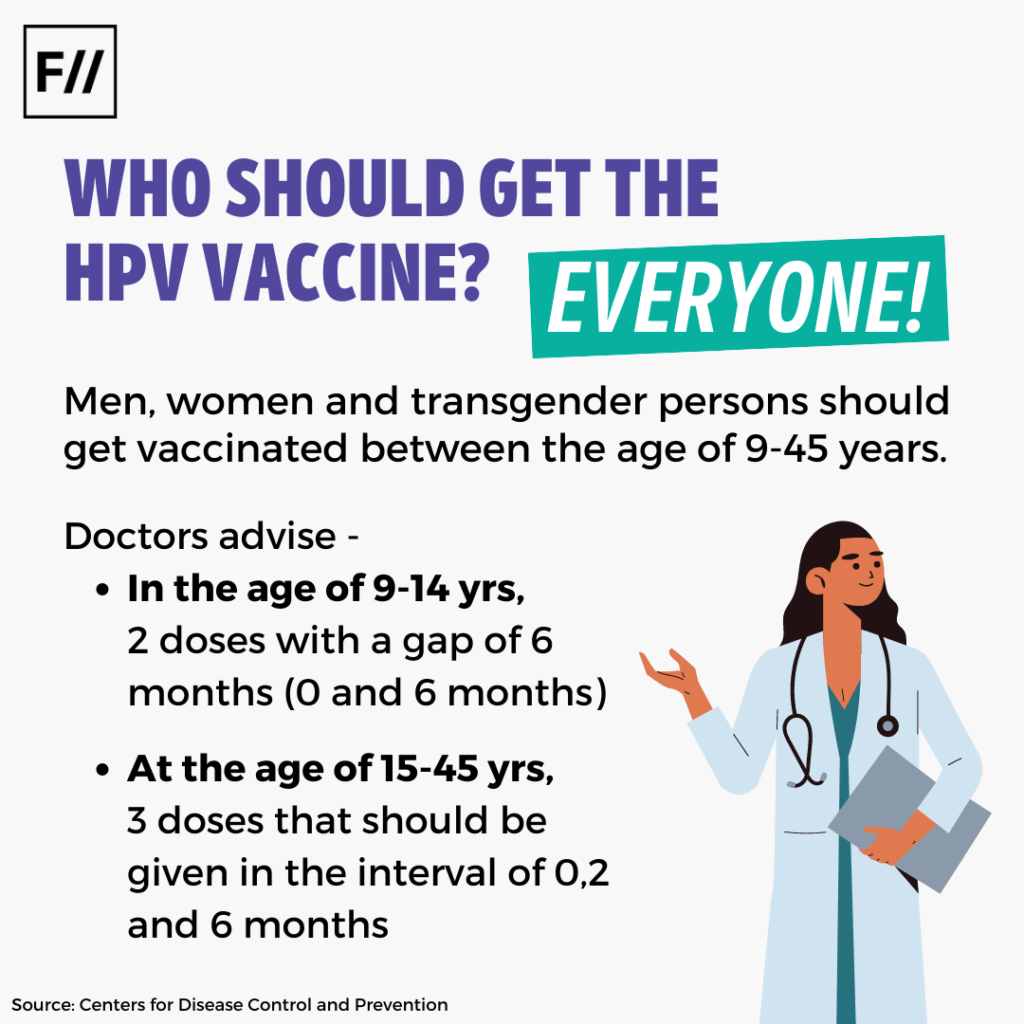
EVERYONE! Men, women and transgender persons should get vaccinated between the age of 9-45 years.
Doctors advise that the HPV vaccine be administered in two doses with a gap of 6 months for people between the age of 9-14 years. Between the age of 15-45 years, three doses are to be given in the interval of 0, 2 and 6 months.
What Are These Vaccines Called?
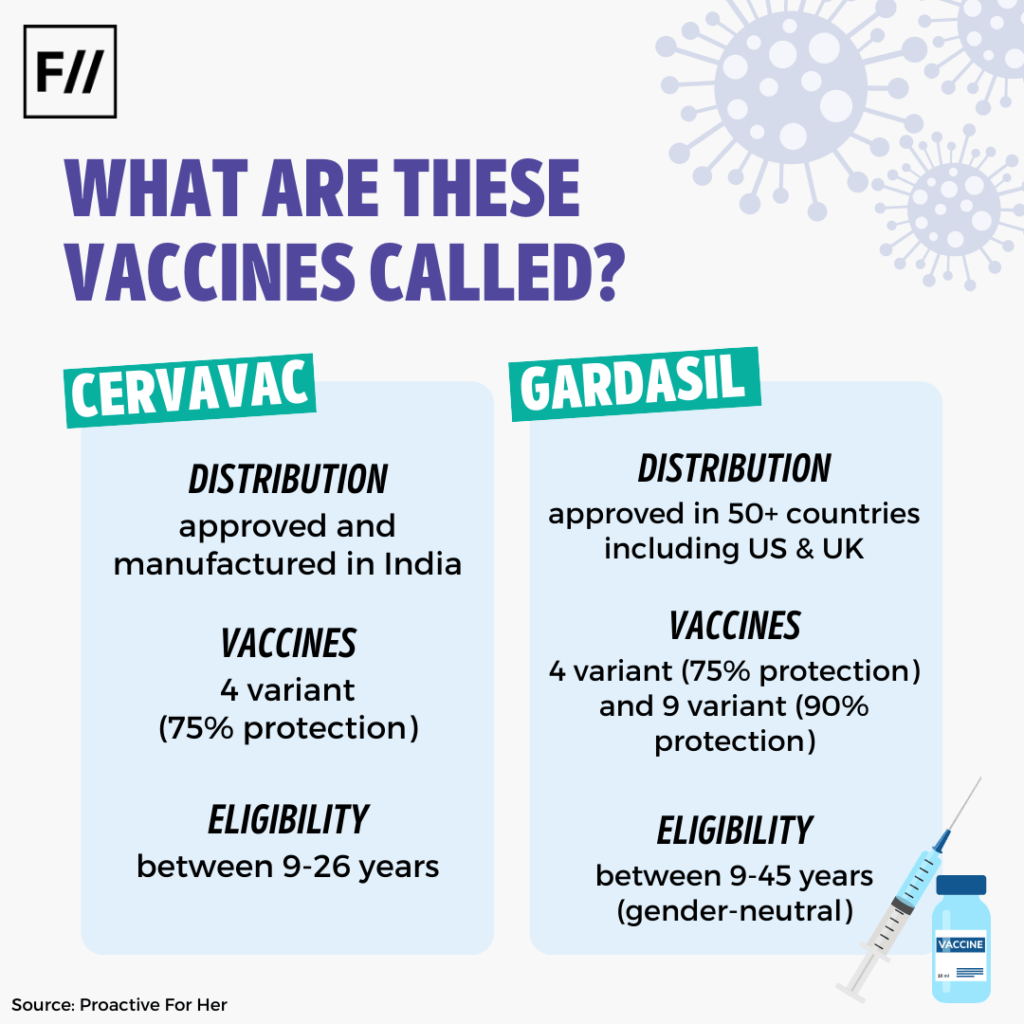
One of the main types of vaccine available in India is Gardasil. It is clinically approved in 50+ countries including the United States of America and the United Kingdom.
In recent news, the Drugs Controller General of India has also approved the Serum Institute of India to market India’s first indigenously developed HPV vaccine, Cervavac.
Despite being around for more than a decade, there is not a lot of awareness around HPV infections that can lead to cervical cancer – a life-threatening disease that can actually be prevented in the first place. There are several myths that surround HPV infections and the vaccine as well. Let’s bunk a few of them!
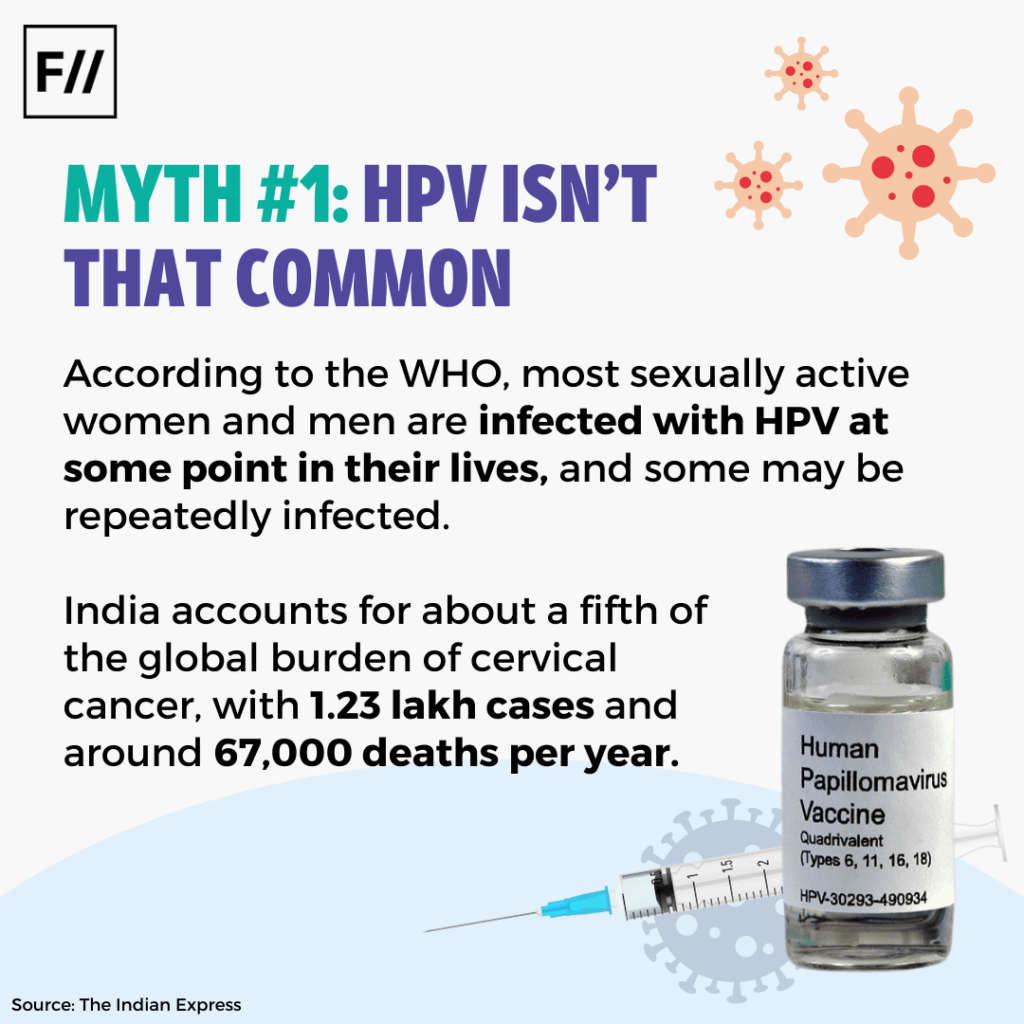
Myth 1: HPV isn’t that common
Fact: As per the World Health Organisation (WHO), most sexually active women and men are infected with HPV at some point in their lives, and some may be repeatedly infected. India accounts for about a fifth of the global burden of cervical cancer, with 1.23 lakh cases and around 67,000 deaths per year.
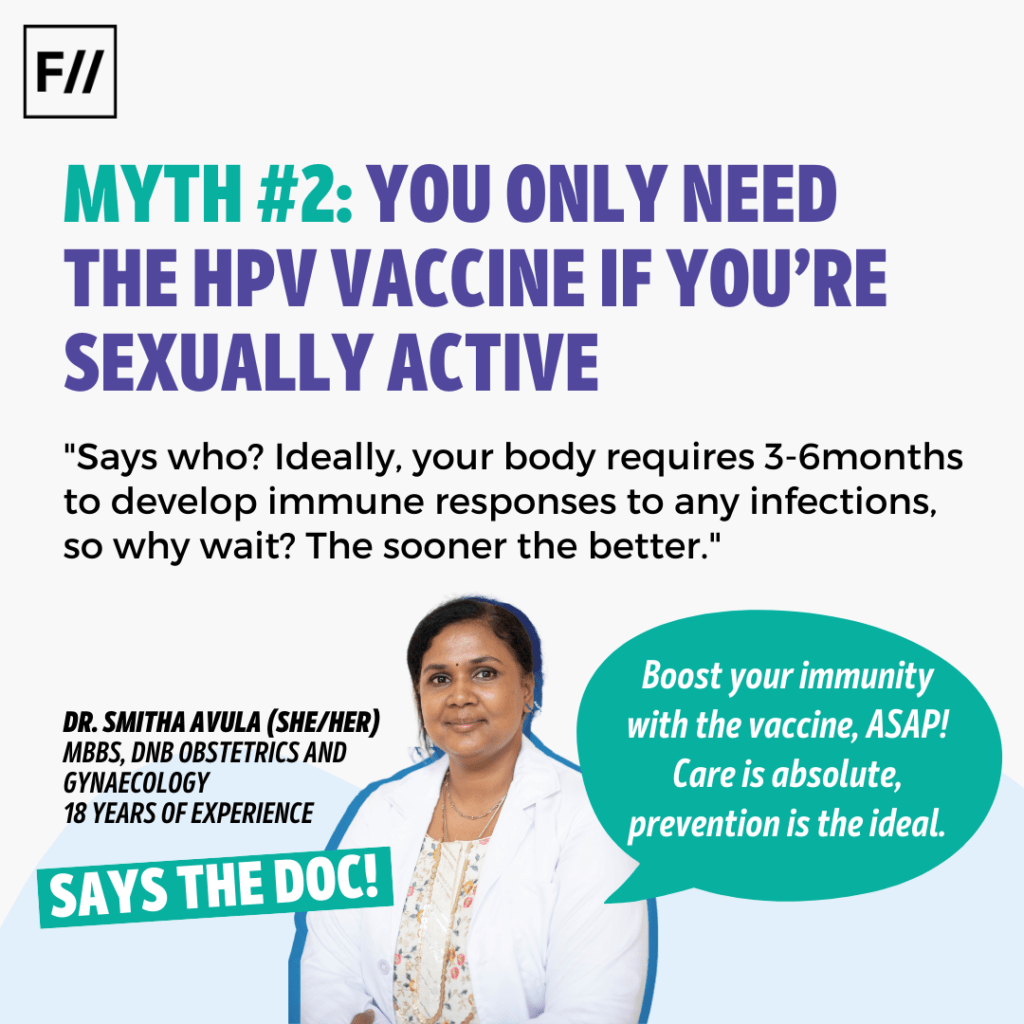
Myth 2: You only need the HPV vaccine if you’re sexually active
Fact: “Says who? Ideally, your body requires 3-6 months to develop immune responses to any infections, so why to wait? The sooner the better“, said Dr. Smitha Avula from Proactive For Her. “Boost your immunity with the vaccine, ASAP! Care is absolute, prevention is the ideal.”
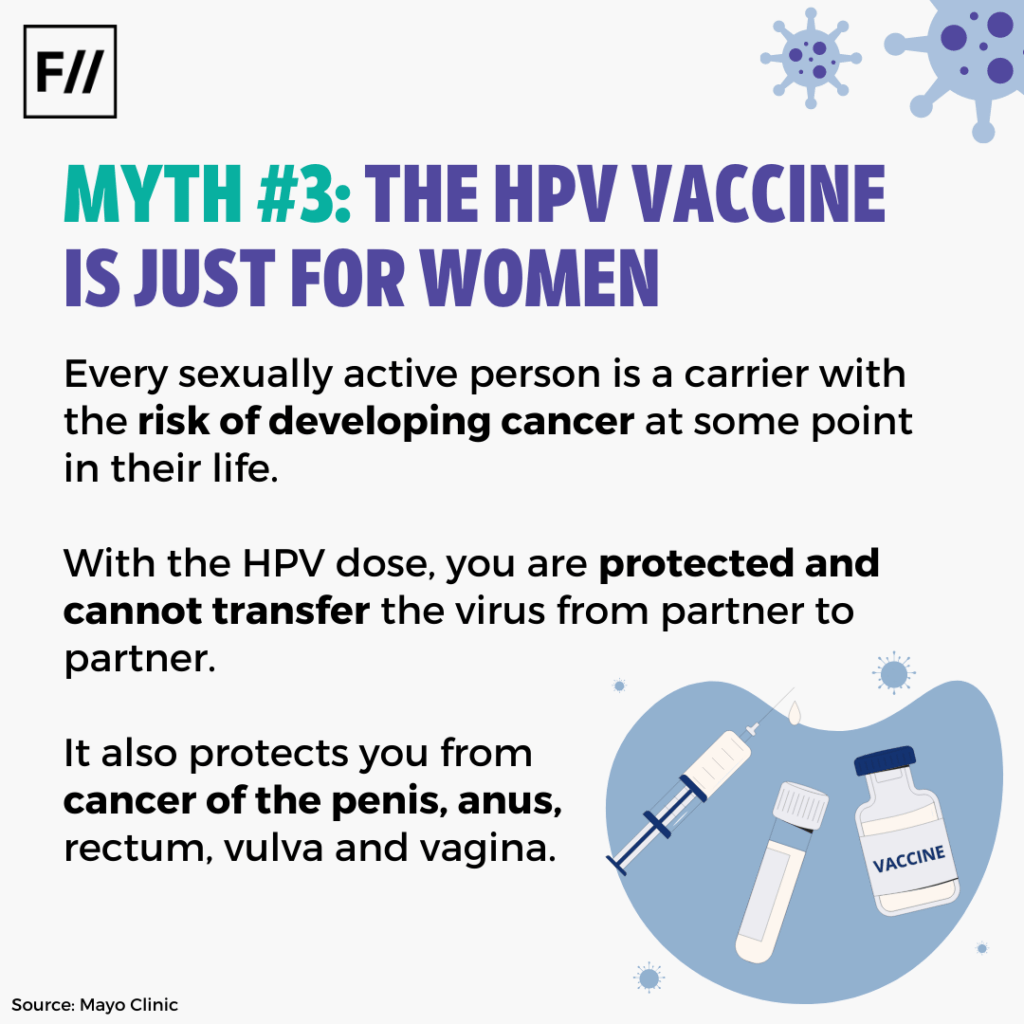
Myth 3: The HPV vaccine is just for women
Fact: Every sexually active person is a carrier with the risk of developing cancer at some point in their life. With the HPV dose, you are protected and cannot transfer the virus from partner to partner. It also protects you from cancer of the penis, anus, rectum, vulva and vagina.
Is the Vaccine Safe?
Yes, it’s safe! Like any other medicine, the HPV vaccine can have mild side effects that subside within a day or two. Common side effects can include pain or swelling where the shot was administered, fever, tiredness or muscle and joint pain.
The HPV vaccine is highly effective for the prevention of HPV serotypes 16 & 18, which cause 70% of cervical cancers. So yes, it is advisable that you get it!
Where To Get The Vaccine From?

We came across Proactive For Her – a digital health clinic that offers accessible and personalized HPV vaccinations at your home. You can check their Instagram page for more details, or book an appointment at www.proactiveforher.com.
About the author(s)
Aishwaryaa is a content producer with a passion for storytelling. She is a keen explorer of digital media and learner of feminism, seeking to drive change and social impact through her work. Her interests lie in culture, gender, and human interest stories. You can find her on Twitter, Instagram and LinkedIn.