Women launch small-scale businesses related to livestock, farming and processing in this tiny village in Maharashtra to reap benefits financially and socially
By Dr Lakshmi Unnithan
Ahmednagar, Maharashtra: Kalpana Sandip Dhawade (37) of Gundegaon in Maharashtra’s Ahmednagar district never wanted to raise hens as a side business. Nevertheless, after climate change triggered crop loss, she decided to enter the fray in 2017.
‘My family was into cultivating our 2.5-acre plot, but we never got any income from it. Erratic rainfall destroyed our crops. That was when I realised the demand for eggs in the market and decided to start a poultry unit by taking a bank loan,’ she says.
Initially, Dhawade reared about 10,000 birds and sold nearly 8,000 eggs every day at the rate of Rs 5 per egg. The profit instilled confidence in her and she decided to get additional birds. ‘My unit now has 12,000 more birds, which will lay about 30,000 eggs every three to four days. In a month, we get around Rs 3 to 4 lakh in turnover, of which roughly Rs 1 to 1.5 lakh is profit,’ she beams.
Like in many other places, both shortage of water and abundance of it have been affecting Gundegaon too. Right now, rainfall is sporadic. So, Dhawade has arranged for a tanker to meet the needs of the unit.
‘Four men work in the unit at a monthly pay of Rs 30,000. We have been using a chicken cage system since 2017. It was purchased using the Rs 40 lakh loan that I had taken, but we did repay the full amount. Our next plan is to establish a fully automatic layer poultry system worth Rs 3 crore,’ she adds.
To ensure the health of the birds, a doctor visits the unit once every 15 days. Dhawade also sells composted chicken manure for about Rs 15 per kg.
To ensure the health of the birds, a doctor visits the unit once every 15 days. Dhawade also sells composted chicken manure for about Rs 15 per kg. ‘I am happy because even my husband assists me in running the business nowadays,’ says Dhawade, who enjoys being an entrepreneur, thanks to the shared learnings of the village women and business ideas from Santosh Bhapkar, a progressive farmer who heads the village collective Sampoorn Shetkari Ghat.
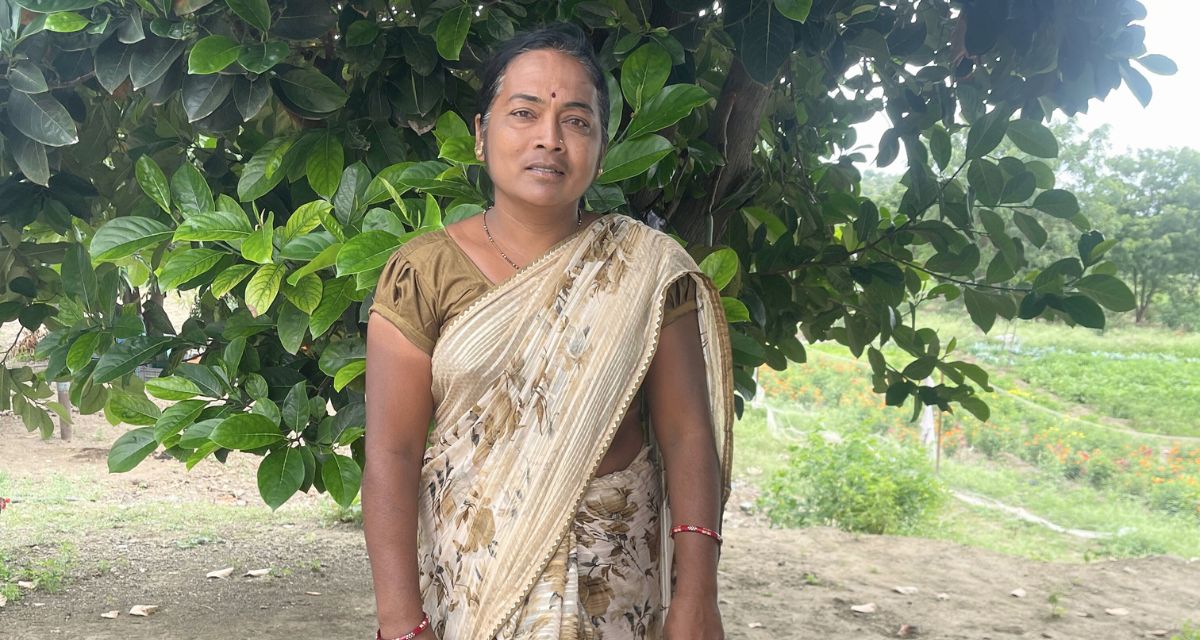

Santosh, also the deputy sarpanch of the village, began his efforts to form the collective in 2005, but it started working effectively only from 2017-18. Both Santosh and his wife Jyothi Santosh Bapkar (35) worked tirelessly to make farmers aware of the adverse impacts their cultivation using pesticides and chemicals had on the soil and the food they grew and ate.
The collective managed to bring 300 farmers, including 100 women, under it, thus transforming 1,800 hectares into fully organic plots. It brought together farmers under a single brand for effective marketing and started wholesale purchase of produce from farmers by offering a 28% extra rate on the total produce. Jyothi studied the trends in the relatively distant markets of Mumbai and Pune to make the most of them. The collective also helped in arranging loans for entrepreneurs.
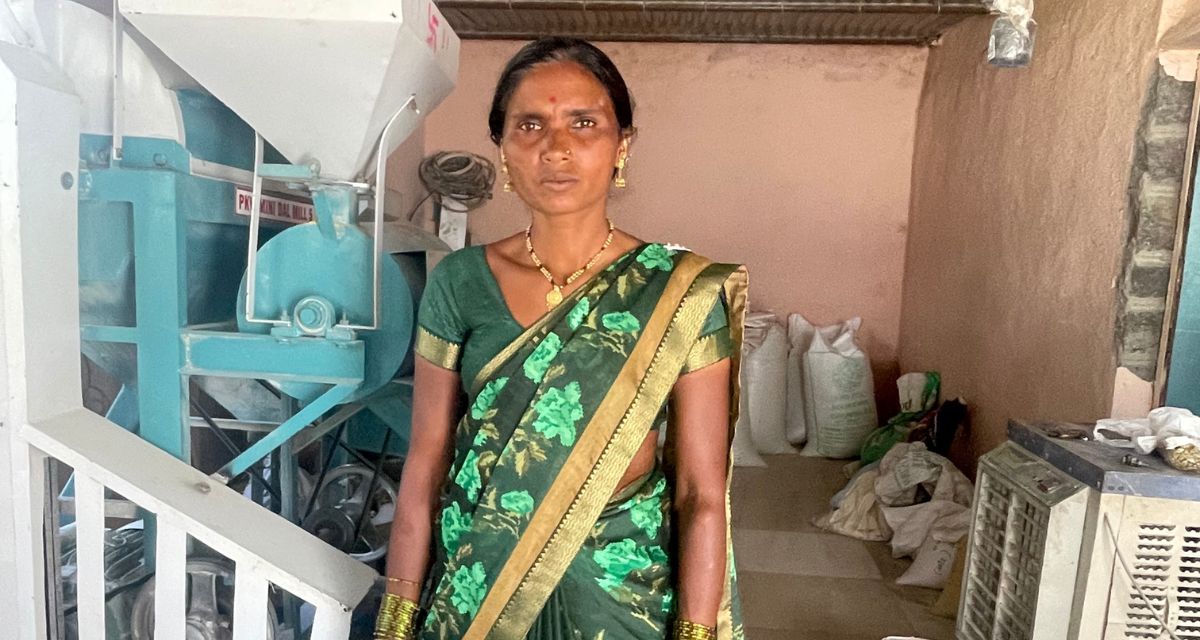
The family of Savita Bapu Choudhary (37) owned very little land, so she came up with the idea of a pulses processing centre. She got help from the collective to arrange loans for purchasing the processor. Since 2017, the centre has been processing pulses, including tur (pigeon pea), moong (green gram) and urad (black gram), thus ensuring constant supply of quality produce sold under the Sampoorn Shetkari Ghat.
‘Mung and urad are harvested in September and October, and Bengal gram [chickpea] and tur in February and June, respectively. I purchased the machine by getting a loan of Rs 2.20 lakh. It splits and polishes the dal, but nowadays everyone likes it unpolished,’ Choudhary says.
The washed dal is dried on the floor before processing. Cleaning and drying take time as it must be done meticulously. ‘In one season, we get roughly 10 quintals of pulses for processing. We are paid Rs 10 per kg as processing cost. We are about to purchase another machine for Rs 2.5 lakh, which can roast chickpeas, make murmure [puffed rice] and shell and salt peanuts. A grader will also be purchased for Rs 25,000… My family made extra income by growing our own pulses,’ Choudhary explains.
Ribeka Shamvel Jawale (30) used to work as a nurse in Pune before returning home to be with her family in Gundegaon.
Ribeka Shamvel Jawale (30) used to work as a nurse in Pune before returning home to be with her family in Gundegaon. Taking a cue from Jyothi’s work, she transformed the family’s 4.5-acre land into an organic farm plot that has vegetables, grains and cotton [GMO seeds] in it. Her vegetables and other produce are sold under the Sampoorn Shetkari Ghat.
‘In the past, I knew nothing about farming,’ Jawale admits. ‘We were in too much debt and had suffered losses as a result of my in-laws’ chemical practices. In the previous year, I took over farming and began to convert tiny areas. Our first attempt, an organic crop of onions, yielded good results. From half an acre of onion, we made a profit of Rs 20,000. We now farm cereals as well.’
‘This money provides us independence, and we feel that we have a better place in our households now. Our husbands confer with us before taking family decisions. The collective has also made us stronger as women,’ says Jawale.
Even without the collective’s help, women in Gundegaon have shown an interest in entrepreneurship, thanks to their determination to break the cycle of poverty by thinking out-of-the box and learning on the job. So now, it is hardly surprising to see the women, once relegated to the kitchens and backyards, gather in small groups in the village square to share their small victories and the challenges they face. Organic farming, collective farming, poultry, small and large agro business centres and value added services have turned out to be their forte.
Organic farming, collective farming, poultry, small and large agro business centres and value added services have turned out to be their forte.
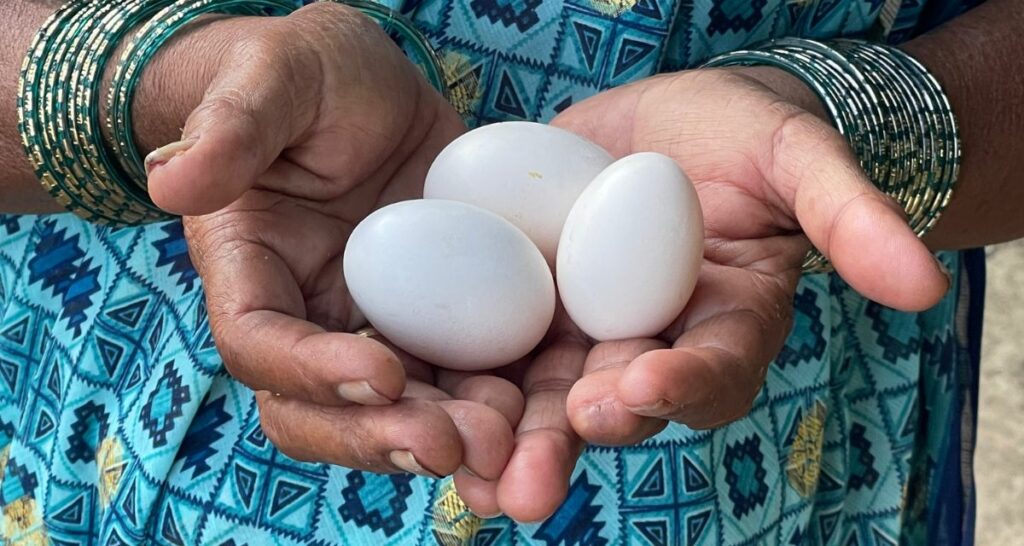
In her hands adorned with green glass bangles, Bhamabai Bhapkar (65) holds the three eggs her free-range hens have just laid. Examining them with care, she says, ‘The money that my hens give is mine; I can do anything I want with it.’
The pride and joy of financial independence that her desi hens bring her are ineffable. ‘I have been into poultry farming at my home for the last 40 years. For my birds, I have a cage made from reclaimed wood. I currently have 45 birds and obtain at least 35 eggs per week, which I sell for Rs 10 each. There was a period when I even had 100 birds with me. This revenue has kept me going all these years.’
Ever since her marriage, Bhamabai has been a resident of Gundegaon. She works at her family farm where horse gram, kidney bean, moong, urad, red gram, groundnut, safflower, sesame, pomegranate, mango and vegetables are grown. At present, her two sons run the farm.
‘The early days were quite challenging. We worked from morning to night, but did not make enough to feed ourselves. I felt obligated to carry out other tasks to supplement our income. That is how the poultry business came about,’ she says.
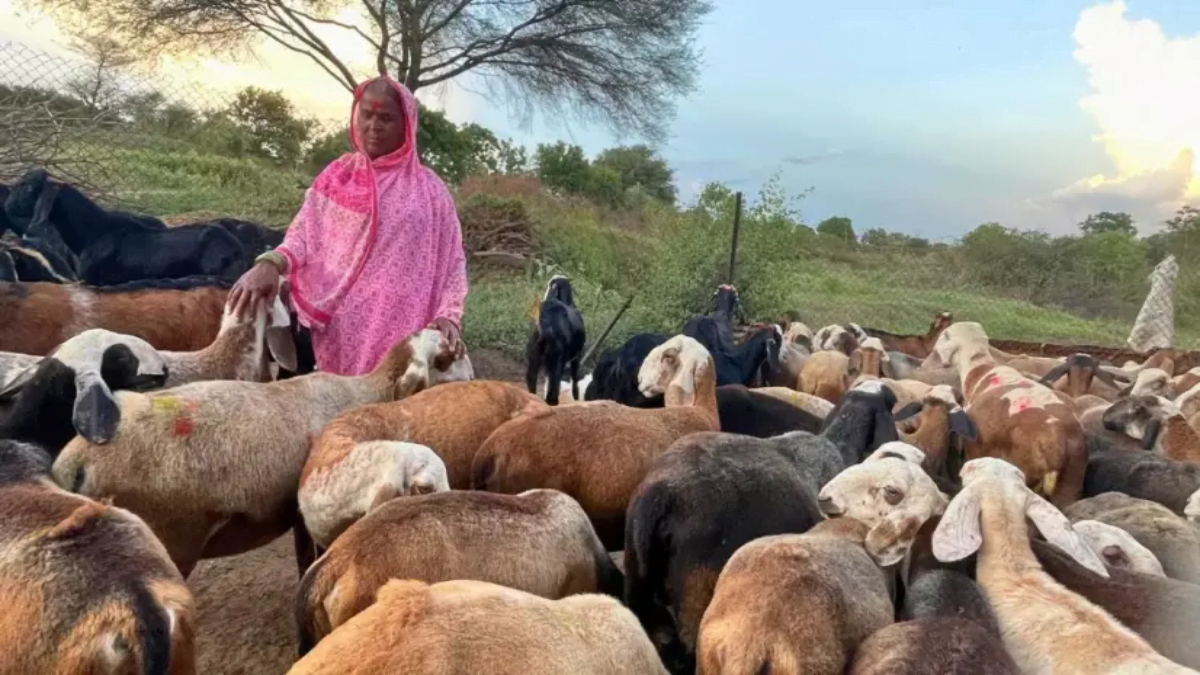
Sindhubai Dhangar (60) owns 60 sheep and goats in all. She belongs to the Dhangar community, a listed Nomadic Tribe in Maharashtra. Climate change has been a major worry for her. On one hand was the heavy and untimely rains, and on the other the shortage of fodder in summers.
‘We travel 50 to 100 km daily and stay on the road for six months, returning only when the monsoons arrive. Farmers are our sole source of support when we relocate to Dahanu, Bhiwandi and Pune in summers. We use tarpaulin sheets and stay in villages for several days. We also carry loads of ration supplies with us,’ Sindhubai explains.
Her husband Balasaheb Dhangar accompanies and helps her to take care of the animals. ‘Each year, the female sheeps and goats give birth to two babies. We make Rs 8,000 to 10,000 each when we sell them. In all, we sell around 120 sheep and make nearly Rs 10 lakh annually.’
This June, Sampoorn Shetkari Ghat has added another feather in its cap.
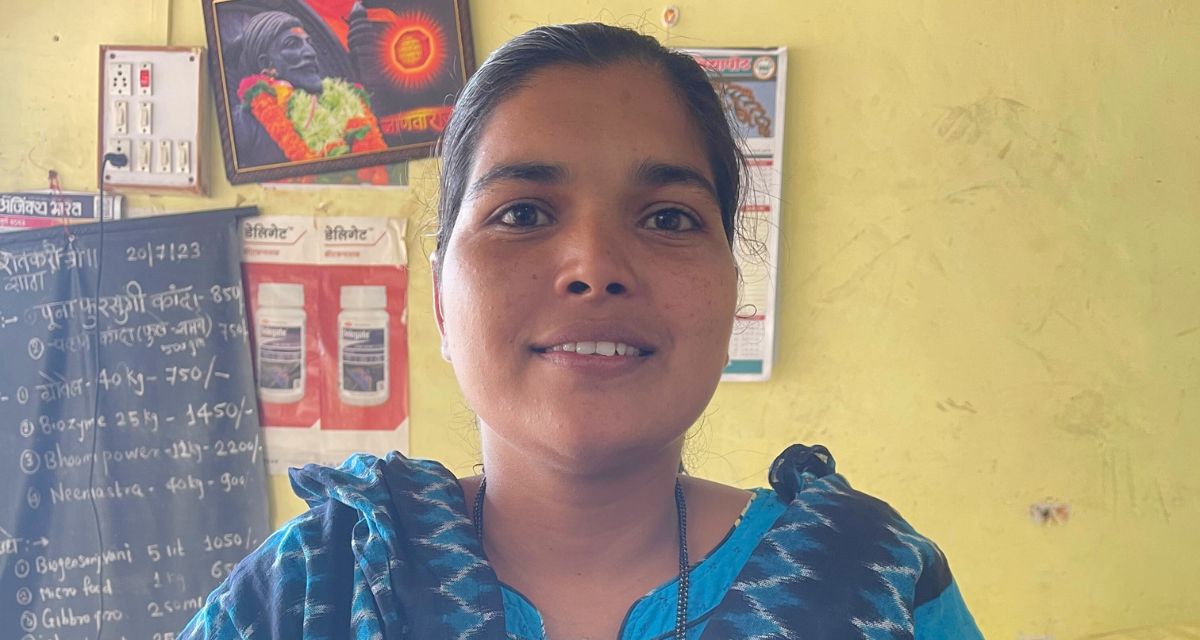
This June, Sampoorn Shetkari Ghat has added another feather in its cap. Shendriya Shetkari, a shop for farmers to purchase organic nutrients and amendments (products to improve soil quality such as livestock manure, plant residue and compost) began its operations from a rented space in Gundegaon’s village square. ‘So far we have made Rs 10 lakh… I am still learning and trying to understand more about business tactics and the economics of running a shop,’ says Jyothi, who manages the shop.
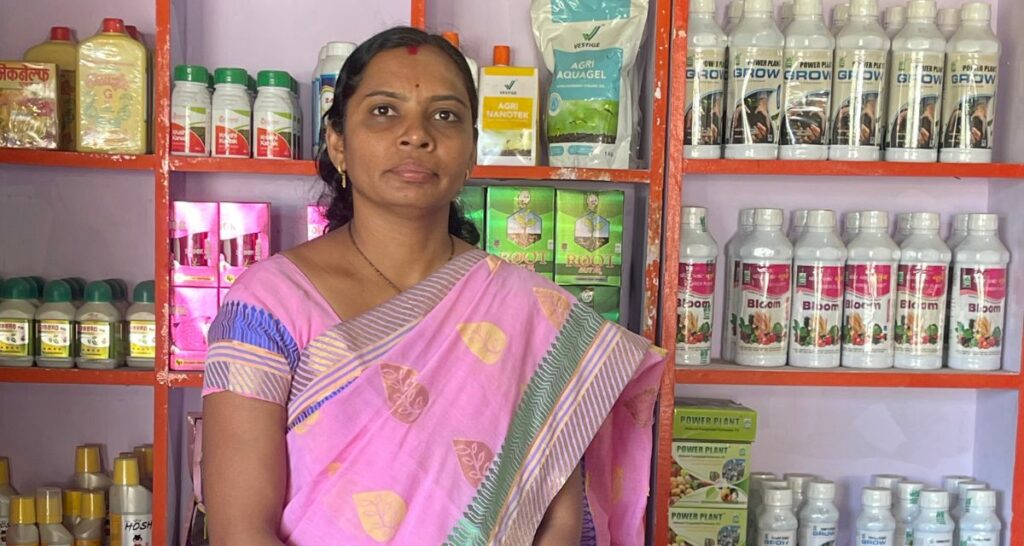

She also works as a field monitor to support women farmers and conducts workshops for them. She acts as a liaison between groups and partners, assisting women to better organise their groups, ensuring their products meet standards, increasing their market presence and helping them gain access to loans. ‘The idea is to help women to contribute to an improvement in the family dynamics,’ says Jyothi.
About the author(s)
101Reporters is a pan-India network of grassroots reporters that brings out unheard stories from the hinterland.