Low participation of farmers in Fasal Bima Yojana and Kisan Credit Card scheme reduces their chance of getting compensation for crop loss
By Paridhi Jain
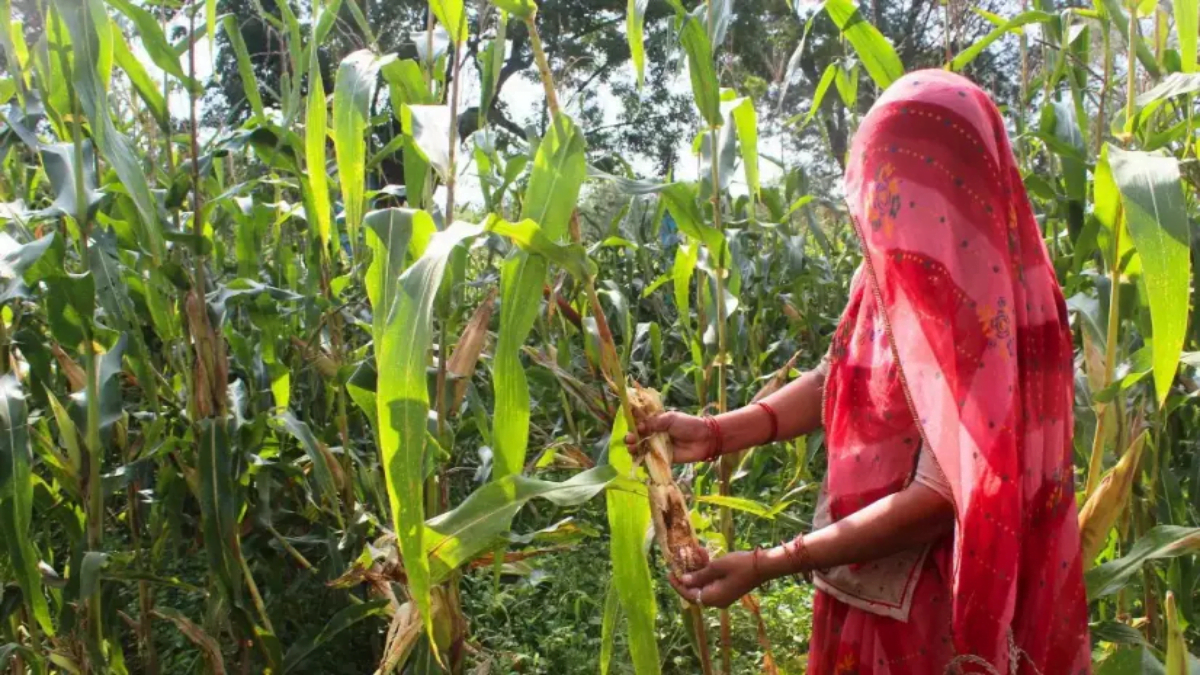
Udaipur, Rajasthan: Looking at his barren fields, Udai Lal Suthar (50) describes the severe agricultural crop losses he suffered this year. Both the vegetables and maize crops that he had cultivated did not survive, thanks to the unpredictable weather patterns and the resultant increase in pest infestations and viral diseases.
‘The initial blow came in June and July, when persistent heavy rains submerged my crops in knee-deep water. The next month, the remaining crops wilted in high temperatures. Finally, in September, when we were harvesting whatever was left of our crops, sudden rains returned, and all of our harvested crops were ruined,’ says Suthar, a resident of Badi village in Badgaon tehsil of Udaipur district in southern Rajasthan.
This year, he incurred a loss totalling Rs 1 lakh as crops in at least eight hectares were damaged. ‘There is nothing left in my fields, they are barren,’ he laments. This situation is also forcing farmers like him to buy vegetables from the markets, adding to their already strained finances.
Erratic rainfall and recurrent dry spells over the last three years have made crop planning exceedingly challenging. This year, Paldi village in Badgaon tehsil saw severe pest infestation in maize and soybean crops.
Erratic rainfall and recurrent dry spells over the last three years have made crop planning exceedingly challenging
Chandkuwar Rajput (40), a local resident, says rainfall in September flattened his maize crop. Most of it was also infested with worms and mites due to the changed weather pattern. ‘Worm infestations have affected not only maize and soybean, but also smaller crops such as chillies. I have been investing a significant amount of money in buying pesticides. Yet, I have incurred a loss of Rs 60,000 to 70,000,’ Rajput laments.
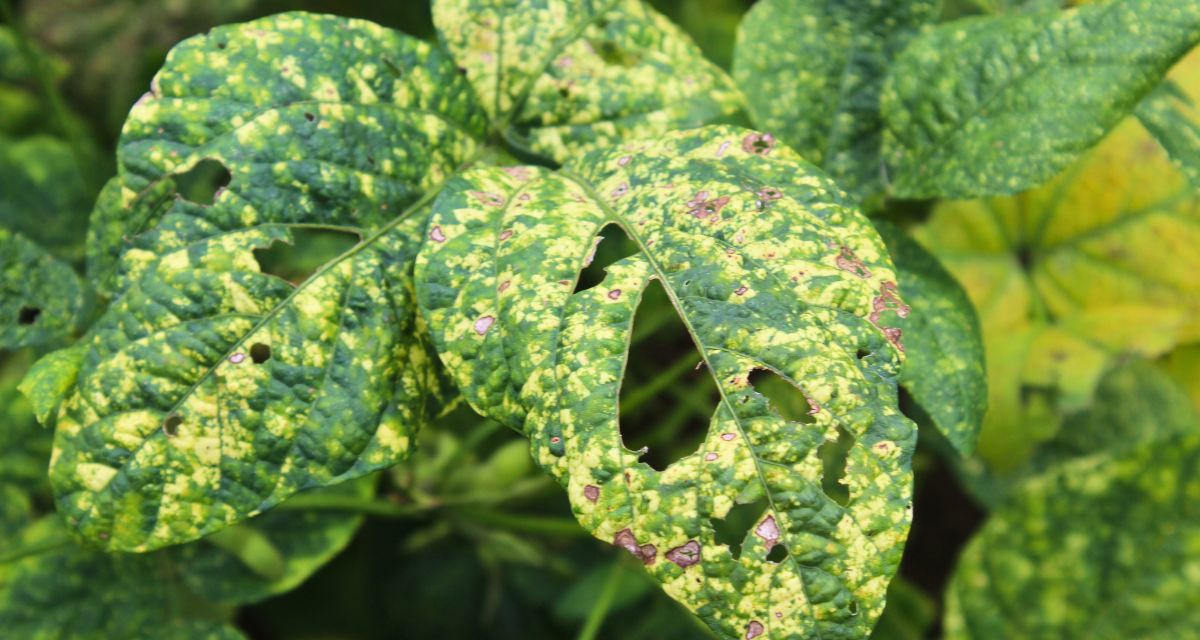

The grim picture of crop loss
Kharif (June to September) is the primary cropping season in Udaipur district. Maize, sorghum, paddy, urad dal (split black lentil), moong dal (green gram), arhar (pigeon pea) and oilseeds such as moofli (groundnut), til (sesame) and soybean are among the major kharif crops here.
According to the information received from the office of agricultural department joint director in Udaipur, the net sown area of last year’s kharif season was 2,32,172 hectares. The total volume of production in that season was 2,86,197 metric tonnes.
As per the department’s estimate, nearly 7,800 farmers in the district have been adversely affected by a combination of monsoon variability and pest infestations. The estimated crop loss encompasses 16,000 hectares of agricultural land this kharif season, with 79% of the damage attributed to extreme rainfall and dry spells, and the rest to pests. In 2020-21, 2,093 hectares were affected by fall armyworm, whereas it was 3,355 hectares in 2022-23.
According to the Udaipur Collectorate office data, the average rainfall this year was 737 mm, which is 159 mm less than last year’s average. Additionally, there were 25 dry days during monsoon this year.
According to Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK), Udaipur, there have been consecutive dry spells in the last four years in the district, with at least 20 to 27 dry days during the monsoon season. Rise in temperatures have increased pest populations as it decreased the pupation time in insects and made them less vulnerable to natural enemies. Similarly, increased rainfall with humidity can lead to fungal and viral diseases in crops.
Dr Deepak Kumar Jain, Subject Matter Specialist, Plant Protection Cell, KVK Udaipur, tells 101Reporters that dry spells and extreme rainfall create a suitable environment for disease pests to proliferate.
‘During my field observations, I have noticed that in the last two to three years, minor pests have become major pests, and new pests have come up. The emergence of invasive species like the fall armyworm have also increased, affecting several crops, including maize, rice and sugarcane.’
‘Controlling fall armyworm is very challenging as it can travel up to 100 km in a single night and lay 500 eggs in one go. Additionally, with increased humidity, viral diseases, including yellow vein mosaic disease transmitted by whitefly, have become common in soybean,’ Jain explains.
On the ways to control them, he says use of improved seed varieties, chemical methods such as Emamectin benzoate and pheromone traps can help. ‘Training sessions are organised to educate farmers on the correct application of pesticides, and subsidies of Rs 500 per hectare are provided for buying pesticides. Moreover, growing Napier grass, application of neem oil and beejamrit, and deep ploughing can prove beneficial,‘ Jain adds.
With research findings from Deshmukh et al. in 2020 underscoring potential human health risks linked to Emamectin benzoate, the question remains as to where to look for the right solution.
With research findings from Deshmukh et al. in 2020 underscoring potential human health risks linked to Emamectin benzoate, the question remains as to where to look for the right solution.
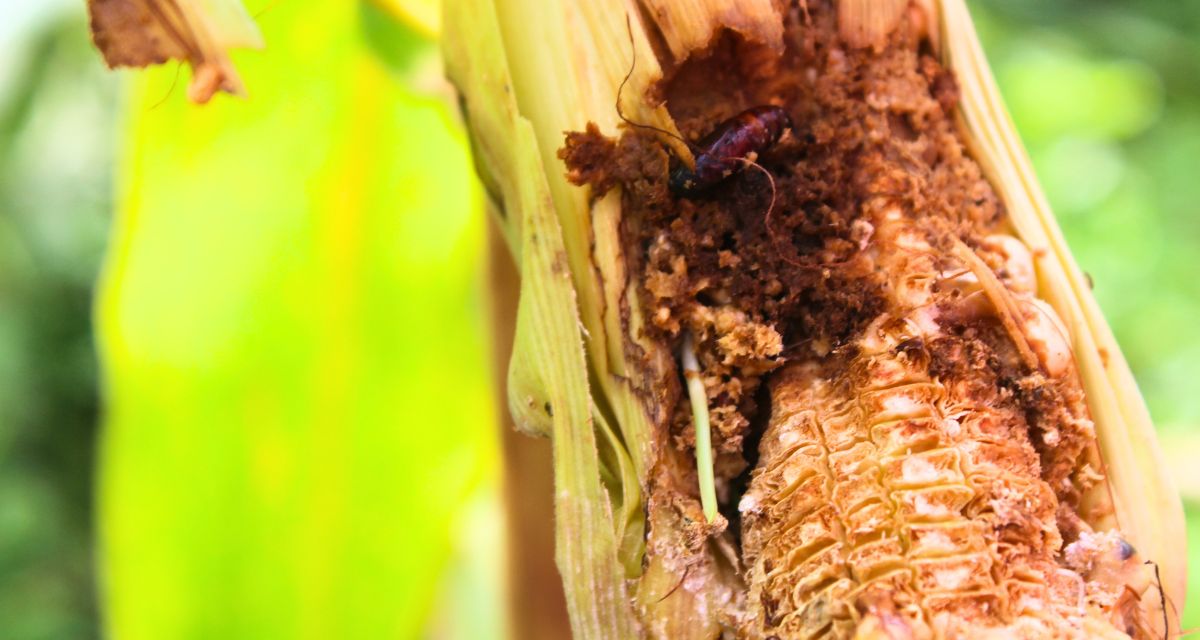

Not many takers for crop insurance
Amid the agricultural crisis, there is a glimmer of hope in government initiatives, including the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY). Though the scheme covers crop loss due to unforeseen circumstances, including natural calamities, the participation of farmers in it is limited here.
About the low participation, Badi gram pradhan (village head) Madan Pandit tells 101Reporters that the procedure for applying under Fasal Bima Yojana is complicated and time consuming, therefore farmers tend to ignore it. ‘Also, the compensation they receive after verification by the authorities is never the amount they initially applied for.‘
Madho Singh Champawat, Joint Director, Rajasthan Agriculture Department, informs 101Reporters that Udaipur has six lakh farmers, and the participation in PMFBY in kharif season this year was of 43,845 farmers, covering only 34,211 hectares. ‘The primary reason is that most of them have small and marginal landholdings. Consequently, they often do not avail of Kisan Credit Cards (KCC),‘ he says.
Participation in PMFBY was earlier compulsory for loanee farmers obtaining crop loan/KCC account for notified crops. However, at present, they can opt out of PMFBY. As farmers are not much interested in taking insurance, they are covered under PMFBY and insured when they opt for KCC now. The farmers in Udaipur have very less land (say 0.5 hectare per person), so they do not benefit much from PMFBY. Moreover, a large number of farmers do not cultivate notified crops.
A similar situation exists regarding the participation of farmers in the KCC scheme. As per the agriculture department records from the current year, only 1,07,348 farmers have acquired KCCs, accounting for just 17% of the total farmers in Udaipur. The average landholding in the district is 0.38 hectares, as per a NABARD report 2018. As a result, the insurance payouts they would receive are rather limited, leading to their lack of interest in the scheme.
As per the agriculture department records from the current year, only 1,07,348 farmers have acquired KCCs, accounting for just 17% of the total farmers in Udaipur.
Champawat goes on to highlight the government’s efforts to increase farmer participation. ‘We have been organising separate camps for both men and women, aiming to promote the cultivation of commercial crops. We have facilitated exposure visits to educate farmers about various irrigation methods, including drip and sprinkler systems. Moreover, clusters comprising several gram panchayats have been formed in Udaipur district to train women farmers. Workshops, with at least 150 farmers in attendance, have been conducted in every village panchayat,’ he says.
According to him, the department also organised krishi upaj mandi at Balicha this June, in which Chief Minister Ashok Gehlot and 32,000 farmers took part. ‘We are actively encouraging people to engage in community and collective farming. Additionally, we are constructing 320 farm ponds to provide irrigation throughout the year, thus mitigating the problem of dry spells.’
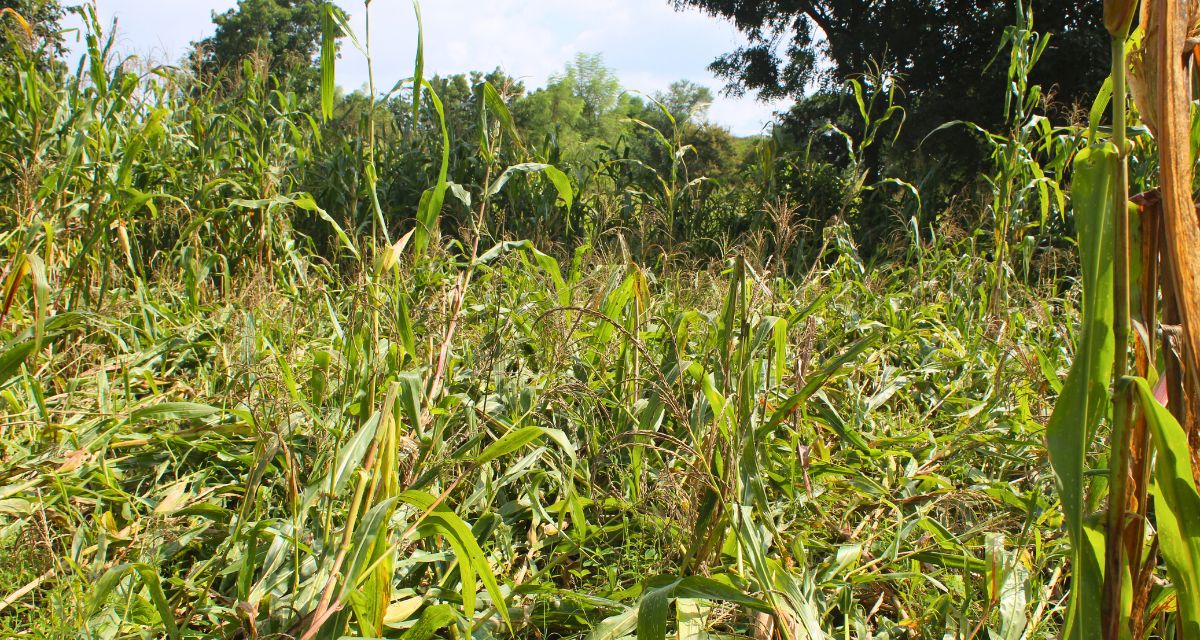

Back to roots
Dr Praful Chand Bhatnagar, Senior Scientist and Head of KVK Udaipur, highlights the success of some farmers in Phalasiya village after they transitioned to cultivating traditional proso millet (chena) and achieved good production with minimal insect attacks.
Heeralal Patel (47), a farmer from Phalasiya, shares his success story. ‘We used to cultivate moong dal and urad dal earlier, but most of it would get destroyed. Last year, we started cultivating chena, and the crop was entirely pest-free,‘ he shares.
Patel gets a yield of 300 kg of millet per season from his field, earning him around Rs 30,000. Seven farmers in the village are now practising millet cultivation, while others have shown a keen interest in cultivating it as their primary crop.
Dr Bhatnagar suggests that reviving traditional cropping systems, especially considering Udaipur’s small landholdings, will help the farmers a lot. ‘Moving beyond cereals, they should adopt integrated cropping systems to include mixed crops such as oilseeds, tubers and pulses in their cultivation,’ he says.
Dr Bhatnagar suggests that reviving traditional cropping systems, especially considering Udaipur’s small landholdings, will help the farmers a lot.
To help address the agricultural challenges in Udaipur, a mix of short-term and long-term measures involving government agencies, agricultural experts, NGOs and the farming community are required.
Paridhi Jain is a Rajasthan-based freelance journalist and a member of 101Reporters, a pan-India network of grassroots reporters.
About the author(s)
101Reporters is a pan-India network of grassroots reporters that brings out unheard stories from the hinterland.