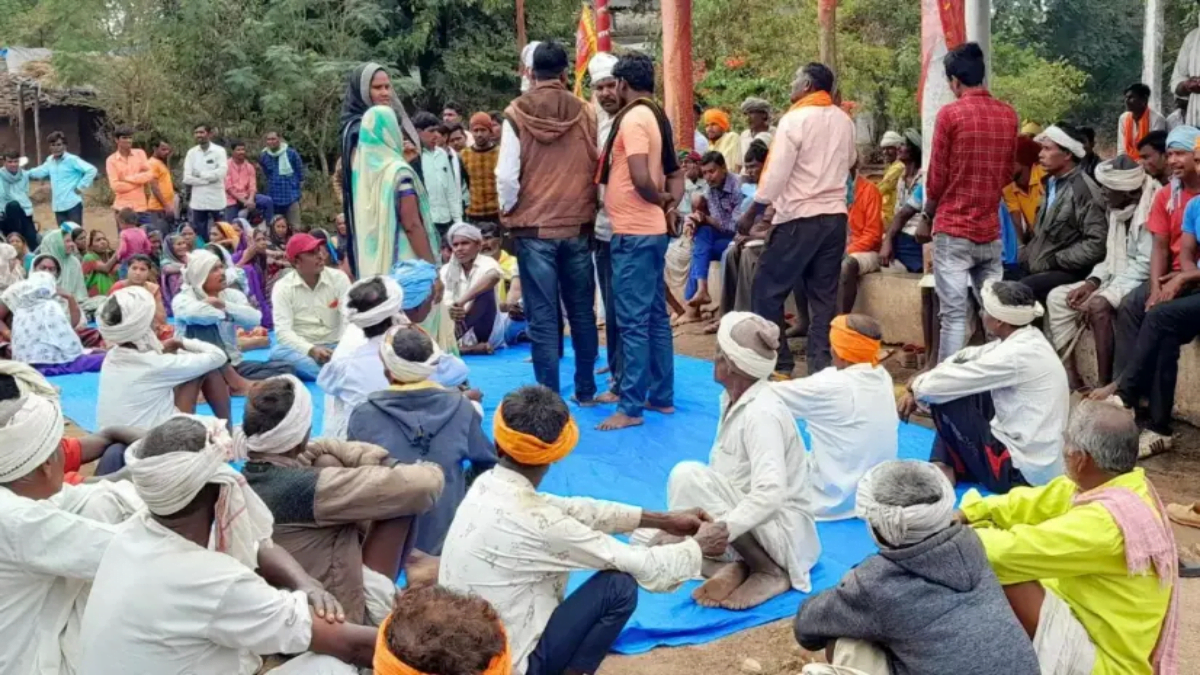
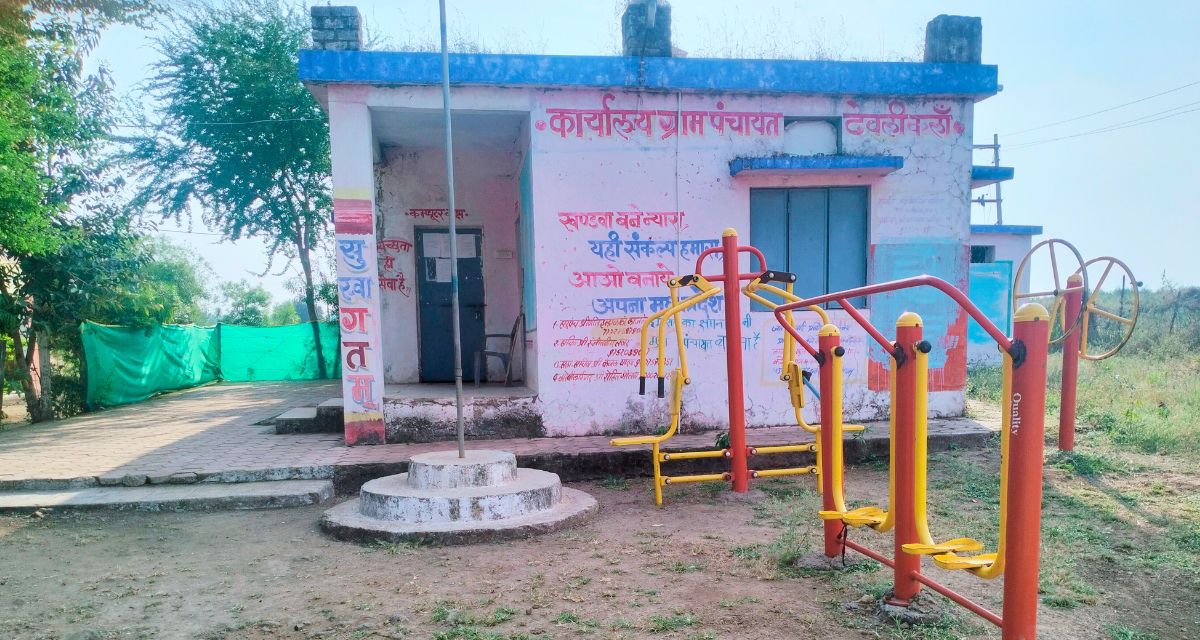
The committees formed under the PESA Act turn a pond into a better revenue generator, remove encroachments, ensure peace through quick and effective resolution of disputes and fast-track distribution of forestland leases
By Mohammad Asif Siddiqui
Khandwa, Madhya Pradesh: Tribal-dominated Devlikala panchayat in Khalwa block of Khandwa district has a five-acre pond that serves the drinking water needs of both humans and livestock and the agricultural needs. For the last 10 years, the pond has also been under fish farming by a Kharkala-based private party. The panchayat had leased out the pond for Rs 30,000 annually.
But things were set to change with the Panchayats (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996, coming into force in Madhya Pradesh on November 15 last year.
But things were set to change with the Panchayats (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996, coming into force in Madhya Pradesh on November 15 last year. Exactly a month later, Devlikala held its first meeting to discuss names for inclusion in committees to be formed in compliance with the Act. Though the committee members had only vague answers when asked about their role at that time, they have come a long way in evaluating the village resources and taking measures to make the most out of them over the last one-year period.

In one such instance, the committees managed to relieve the pond, constructed almost 50 years ago, from the clutches of a private party as its members assessed that the lessee was earning much after getting the pond year-after-year at comparatively meagre rentals. The land committee estimated that fish worth about Rs 2 lakh was reared every year without giving any fish feed.
As the land committee is responsible for changes in the use of government or community land, and deals with matters of transfer, lease, contract, agriculture, sale and mortgage of land, it decided to take action. After discussions with experts, the committee took its own decision that the pond will not be given for contract fish farming. Instead, the village panchayat itself will do fish farming to generate more income that can be invested back into the development works of the village.
‘When other means became available, the reliance on the pond for irrigation reduced. Later, the panchayat gave it for contract fish farming. Everything went well until the contractor started to wield monopoly over the pond. The situation became such that even cattle could not access the pond in summers. When villagers complained, the panchayat did not heed to them. After the implementation of the PESA Act, we unanimously banned the leasing of the pond,’ land committee member Bisu Ghisia explained.
Devlikala’s PESA Act mobiliser Rohit Gautam told 101Reporters that the leaseholder prevented villagers from entering the pond. ‘On July 27, the sarpanch and secretary announced the pond auction. However, Dayaram Patil, the chairman of the water committee formed under the PESA Act, decided with everyone’s consent that the auction should be stopped. Patil said the pond produced 20 quintals of fish. Neither fish seeds are put in nor feed given to them. The committee believes that the sarpanch and secretary are in collusion with the lessees, due to which they had been continuously making benefits,’ Gautam said.

The committees formed under the PESA Act also have their eyes on other resources in the village. Land committee member Hiralal Patil said they have been looking into cases of encroachment. ‘Eight months after the implementation of PESA Act, an individual from Malhargarh occupied a 20×40 sq ft land near the main market of the village and started construction. When the matter reached the committee, we passed a resolution against it on August 10. Subsequently, the building was demolished,’ he detailed.
After dealing with the encroachment, the committee members also informed Khalwa Police Station, where a case was registered against the encroacher.
Ever since the PESA Act came into existence, village disputes are being resolved locally.
Ever since the PESA Act came into existence, village disputes are being resolved locally. Peace committee president Champalal Palvi told 101Reporters that the villagers were assured that all disputes would be resolved at the panchayat level ever since the committee started functioning.
‘This has increased their confidence. Now, village disputes are not reaching the police station. Earlier, about two to three cases used to reach the police station every month. Now, every dispute is being resolved at the local level among its own people,’ Palvi claimed.
Suraj Kasde, chairman, forest resource and control committee of Chikatlai in Devlikala panchayat, said the village atmosphere is better than before. ‘Patronage of the panchayat has also reduced. Earlier, we had to make rounds of the panchayat and go to Devlikala for even the minutest of things. Special meetings also used to be held in Devlikala only. But under the PESA Act, meetings have started to take place in our village itself.’
Kasde said the sarpanch and secretary used to scold when someone asked for the accounts of work done. ‘In the general meeting held before the implementation of the PESA Act, when we asked for information about the gravel road built in our village, the sarpanch ended the meeting abruptly. There was an uproar, but it had no effect on the sarpanch and secretary,’ he alleged.
After the implementation of the PESA Act, people’s work is being done at a faster pace. Kasde claimed about 50 villagers have been demanding land leases for the last 15 years. ‘The forest dwellers have been farming for many generations, but till now they have not received the leases for those lands. After the formation of the committees under the PESA Act, the work gained momentum. So far, leases have been approved to eight villagers,’ he said.
Punaibai Shobharam(64), a beneficiary, said her husband had demanded for lease until his death. But even after his death, she did not get it. After the committee came into existence, she started to get her widow pension, Moreover, she is all set to receive her lease document. ‘It seems as if our government has come, a government that thinks seriously about us,’ she said elatedly.
Earlier, for all panchayat-related works, the villagers had to go to Kharkala. However, after the formation of committees under the PESA Act, the villagers now have a better system in place.
Devlikala has its 50% seats in panchayat elections reserved for women. Hence, the sarpanch is Indrakala Kajle, who hails from Kharkala. Like in most panchayats of Madhya Pradesh, her husband Pyarelal Kajle manages all the work. Earlier, for all panchayat-related works, the villagers had to go to Kharkala. However, after the formation of committees under the PESA Act, the villagers now have a better system in place.
101Reporters tried to contact Indrakala about the allegations raised against her, but her mobile phone was either out of network coverage or switched off. When panchayat secretary Ranjit Tanwar was contacted, he refused to reply to the allegations saying he was busy with family-related work.
Mohammad Asif Siddiqui is a Madhya Pradesh-based freelance journalist and a member of 101Reporters, a pan-India network of grassroots reporters.
About the author(s)
101Reporters is a pan-India network of grassroots reporters that brings out unheard stories from the hinterland.