Posted By Dr S. Natesh
September 11 signifies a very important landmark in the history of India’s environmental movement. It’s said on this day, back in 1730, in a tiny desert village near Jodhpur, 363 Bishnoi people led by a brave woman resisted the cutting down of khejri trees, among others, by the king’s men, preferring instead to lay down their own lives rather than allow the desecration of their environment. In 2013, the Department of Environment and Forests declared September 11 as National Forest Martyrs Day. This saga of supreme sacrifice has had a cascading effect in terms of more recent environmental movements across India, notably the Chipko Andolan. But before we get to the story of how several Bishnoi people sacrificed their lives for the khejri trees, we need to understand the Bishnois’ connection with the environment.
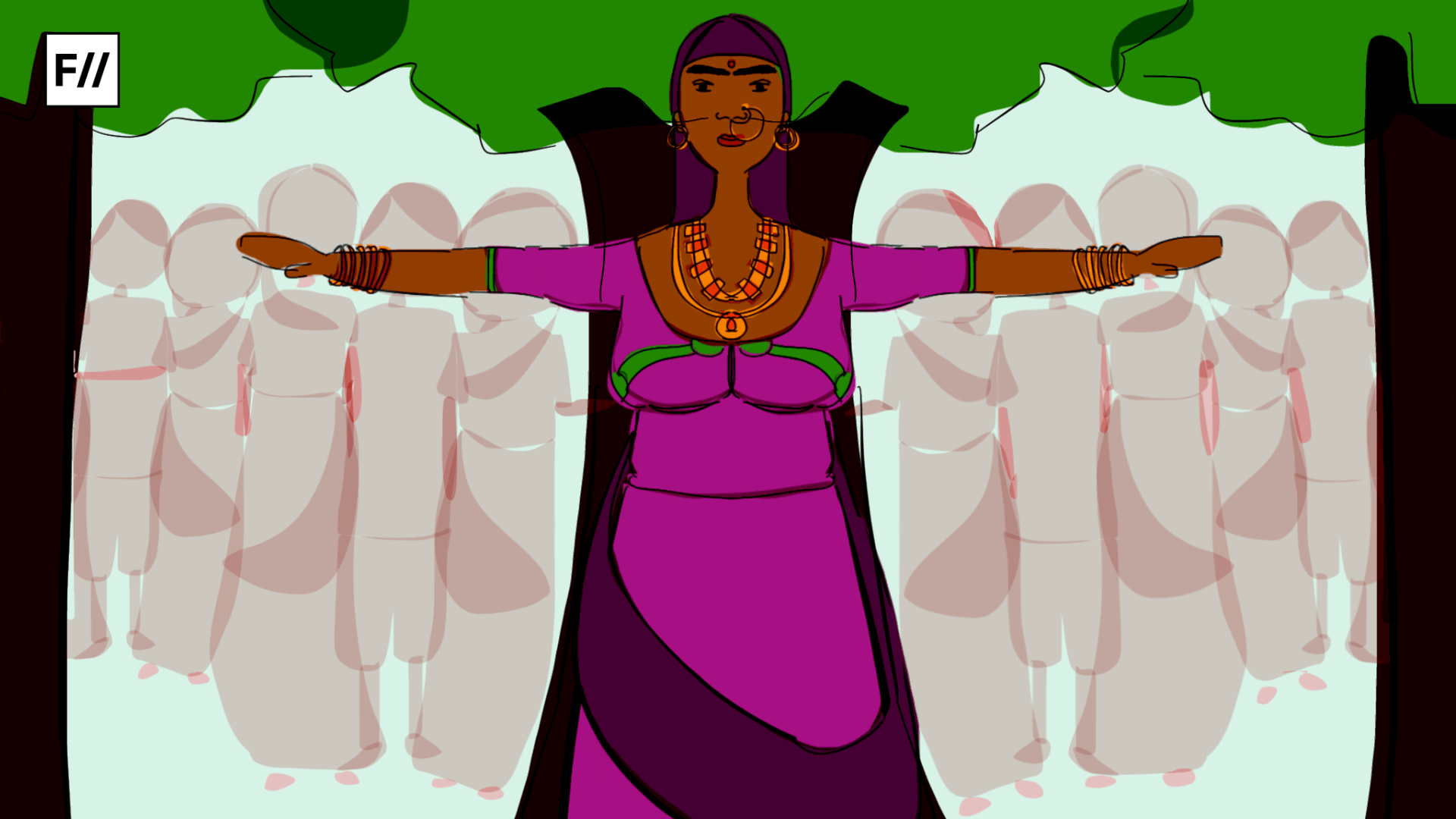
It’s said on this day, back in 1730, in a tiny desert village near Jodhpur, 363 Bishnoi people led by a brave woman resisted the cutting down of khejri trees by the king’s men, preferring instead to lay down their own lives rather than allow the desecration of their environment.
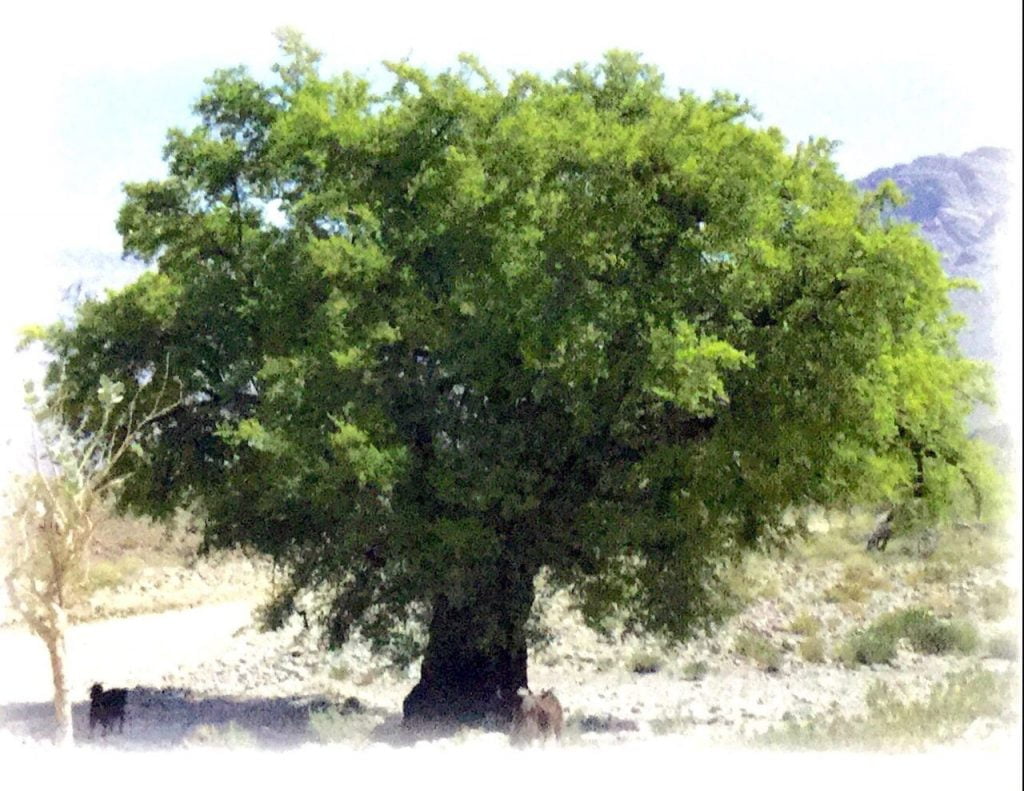

The Arid Thar
Over 60 per cent of the Great Indian Desert (Thar Desert) lies in Rajasthan. With precipitation annually fluctuating widely, the terrain is generally infertile. Summer temperature soars to 500C bringing with it swirling dust-laden winds, often blowing at velocities of 140–150 km per hour. Amid a fragile scrubby vegetation, trees are few and far between—the most important being Khejri (Prosopis cineraria) because of its many benefits. Blackbucks and chinkara gazelles are found here along with partridges and quails.
Amid a fragile scrubby vegetation, trees are few and far between in the Thar—the most important being Khejri (Prosopis cineraria) because of its many benefits. Blackbucks and chinkara gazelles are found here along with partridges and quails.
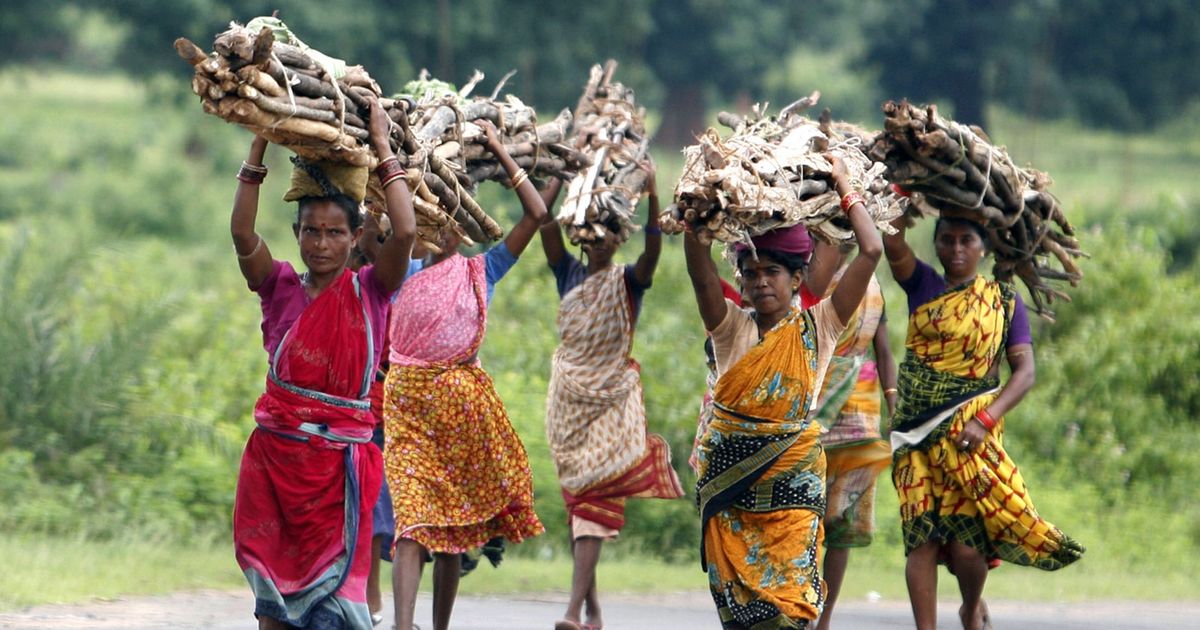
This inhospitable terrain is also home to the Bishnois, identifiable by their distinct dress style. Traditionally, the men wear white, and the women are attired in ghagra-cholis and veils with particular patterns of red and yellow. The women also wear uniquely characteristic half-moon-shaped nose rings that cover their mouths. They are followers of Guru Jambheshwar, a fifteenth-century seer, whose 29 commandments define their ethos. The word ‘Bishnoi’ itself is derived from bis (twenty) and noi (nine), and thus they are the ‘twenty-niners’. Seven of these commandments teach good social behaviour, 10 address personal hygiene and health practices, four provide instruction for daily worship, and eight are related to conserving and protecting animals and trees and encouraging good animal husbandry. The last-mentioned set of the principles are what enable them to live harmoniously and comfortably within this inhospitable terrain. A photograph of a woman breastfeeding a blackbuck along with her child went viral in 2019. In fact, Bishnois spare no effort in protecting trees and wild animals. No wonder then that Bishnoi villages are greener, and it is a common sight to find herds of deer and nilgai moving freely.
Also read: Revisiting Deccan Development Society: A Tale Of Dalit & Marginalised Women Saving The Environment
The Sacred Khejri
The Khejri tree holds a special place in their lives, and cutting down or lopping its branches is taboo. This small evergreen tree has been hailed as the lifeline of the Thar desert. It is a source of shade; its leaves provide fodder to camels, goats, cattle and other animals; its pods are edible and the wood is used as fuel; its roots fix atmospheric nitrogen, making the soil fertile. The khejri is, therefore, invaluable to desert economy and ecology. Revered as shami since Vedic period, the tree features prominently in both the Ramayana and Mahabharata.
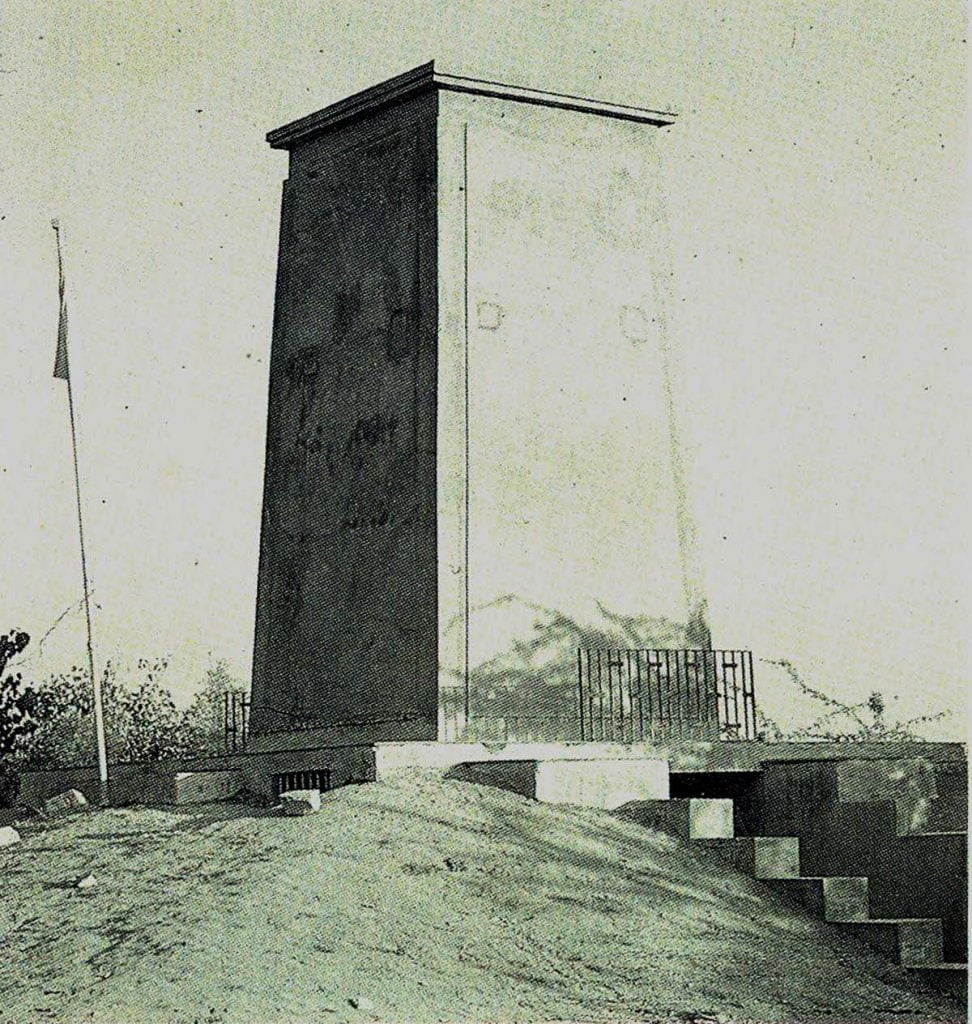

The Great Sacrifice
About 18 km from Jodhpur is the small Khejarli village. Like other Bishnoi villages, this one, too, is green and especially rich in khejri trees. The morning of September 11, 1730, when strange men with large axes descended on the village on their horses, Amrita Devi rushed out of her house—as did other villagers—with her three daughters in tow to see what the excitement was all about. She learnt that these were the king’s men, with the mission to cut down and carry off the khejri trees to Mehrangarh Fort in Jodhpur. Maharaja Abhay Singh had decided to build a new palace and was in need of wood to keep the kilns going for construction material.
It was common practice then to burn lime in a kiln at very high temperature to obtain quicklime which, when mixed with sand and water, would become mortar used to bind and hold together stones and bricks for construction. To keep the kiln going, they needed plenty of wood. This posse had reached Khejarli for an assured supply.

Since cutting or injuring trees, especially khejri, is against Bishnoi dharma, Amrita Devi remonstrated with the men, but they were unmoved. She then hugged a tree and declared that even if she sacrificed her life to save just one tree, it would be a good bargain. The unyielding men nonchalantly chopped through her body to cut the tree. Her three daughters, though utterly shocked to see their mother’s severed head, followed in her footsteps bravely, hugging trees and meeting the same end. This made no impression on the royal party, and they continued their task with renewed vigour. The news spread like wildfire and Bishnois of 83 villages gathered at Khejarli. They held council and decided that for every living tree to be cut, one Bishnoi volunteer would sacrifice her or his life. In all, 363 Bishnois from 49 villages became martyrs that day. The very soil of Khejarli turned red with their blood.
Since cutting or injuring trees, especially khejri, is against Bishnoi dharma, Amrita Devi remonstrated with the men, but they were unmoved. She then hugged a tree and declared that even if she sacrificed her life to save just one tree, it would be a good bargain.
When the king heard the dreadful news, he put an end to the felling of trees. Honouring the courage of the Bishnois, he apologised to the community, and issued a decree engraved on a copper plate prohibiting forever the cutting of trees and hunting of animals within and near Bishnoi villages. That protection is still valid today, and Bishnois continue to guard their biodiversity fiercely.

The First Environmentalists
The Khejarli sacrifice was characterised by total non-violence, or ahimsa, on the part of the Bishnois who stood up to perform what they considered their bounden duty. For them, every plant or animal is a living being just as humans, and hence deserves to be protected. This served them well as it fosters a better relationship between human beings, their environment, their religious beliefs and each other, allowing all to live harmoniously. Today experts call this ‘sustainability’, and have labelled Bishnois as ‘India’s first environmentalists’. Yet, within their community it is simply understood to be their dharma.
Also read: Remembering Chipko Movement: The Women-led Indigenous Struggle
Nearly 230 years after it happened, the Khejarli story inspired another environmental movement—the Chipko Andolan (1973) in the Tehri-Garhwal Himalaya. This, in turn, spawned the Jungle Bachao Andolan (1982) in Bihar and Jharkhand, the Appiko Chaluvali (1983) in the Western Ghats of Karnataka, and other similar protests. All these were aimed at preserving and protecting the natural environment and resulted in changing public policies. The ‘tree-hugging’ tactic of the Chipko Andolan and its messages gained popularity in many countries beyond India’s borders, leading to protests in Switzerland, Japan, Malaysia, The Philippines, Indonesia and Thailand.
Surely, Amrita Devi would have approved.
This article is part of Saha Sutra on www.sahapedia.org, an online resource for Indian arts, culture and heritage.
Dr S. Natesh is a botanist with a passion for documenting the heritage trees of India and plants that influenced history. He taught at Delhi University before moving to the Department of Biotechnology, GoI, where he headed several divisions. Currently he works at the DST Centre for Policy Research at IIT Delhi. His book on the heritage trees of India is slated to be published in 2021 with Roli Books.
Featured Image Source: Ritika Banerjee for Feminism in India
About the author(s)
Sahapedia.org is an open online resource on the arts, cultures and heritage of India.



The Kejri movement narration is astonishing and invaluable. For the first time I came across this hidden history. I feel it should be a lesson for primary school children across the country in the mother tongue languages, which will seed the importance of afforestation and need of saving the innocent animals.