Posted by Ashif Shaikh
There are 650 districts in India. However, most nonprofits work only in a few districts. Given how large our country is, there are only two types of people that can work towards creating change at scale – the communities that are facing the issues first hand, and the government.
The government has not been able to work on issues related to social justice in the last 60 years. Perhaps they think that this is not important enough, or there is no political will to do it. So, we at Jan Sahas, chose to involve the community.
We realised that if issues around social justice had to be taken to scale, and if we wanted to create deeper impact,we needed to involve the communities affected. If it didn’t become the community’s own initiative, or if they kept thinking that some civil society organisation or government agency would come and work on their issues, it would never be sustainable.
That’s why in 2001, we started a national campaign named Rashtriya Garima Abhiyan. Centred around the idea of dignity, this campaign was aimed at mobilising Dalit manual scavengers, all of whom were women. We wanted to empower them to move out of this work and enable them to scale up the programme on their own. We thought that working with manual scavengers would be a good entry point to work on ending exclusion.
We talk about people living in dignity, but most of us understand this as, if we offer wages, we automatically provide dignity. The government also seems to think along the same lines. They offer anywhere between a few thousand rupees to a lakh of rupees in the form of various schemes.
Like they say in the gender discourse – if you want to end sexual violence, you have to get the male members of the community involved.
But caste-based marginalised communities in our country have faced historical injustice – not just for the last five-six generations, but for the last 2,500 years. Even if they earn money and stop doing caste-based work, the social stigma never goes away. Even if the person becomes a collector, or starts an enterprise, the discrimination continues.
We need three types of rehabilitation
If people have to come out of caste-based work, they need three types of rehabilitation:
1. Economic or livelihood rehabilitation
In the caste-based work of manual scavenging, the biggest issue is that the oppressor or employer provides them food, clothing and shelter. In rural India, they get two rotis every day, clothes twice a year – during Holi and Diwali, and the panchayat gives them a place to stay, So, in essence, their basic needs of roti-kapda-makaan are taken care of by the person or the institution that employs them. What this means though is that they are unable to negotiate with their employers.
If you are going to get paid in cash for work, you can negotiate. For instance, if the employer says ‘I will give you INR 20’, you can say, ‘No, I will charge INR 50’. But if your life itself is dependent on what they give you, then you can never negotiate.
Therefore, if we have to start changing the way caste is viewed and reinforced, we have to start with economic rehabilitation. If marginalised caste groups get work which pays them in cash, they can negotiate the terms for their wages, working conditions, dignity and relationships at the workplace.
However, this is only step one. The second, and more important one, is social rehabilitation.
2. Social rehabilitation
The government never thinks about this aspect. Under social rehabilitation, if someone gives up their (caste-based) work, they should be given work that factors in the social aspect as well.
For instance in 2013, we appealed to several state governments; we said that when you appoint ICDS workers and helpers – positions that do not require an educational background, offer INR 3,000-4,000 monthly salary and where the employee has to be a woman, give priority to the women from the manual scavenging community. These women could prepare the meals provided under the ICDS scheme, and all children regardless of their caste would eat that food.
This process was started in Uttar Pradesh but many powerful groups forced the state to rescind the order; today it is no longer compulsory. In Madhya Pradesh on the other hand, while there was some struggle to start with, it has now been firmly established in many districts.
The discrimination extends across several government schemes. In many villages, where the PMAY is being implemented, Dalit communities are given homes in a separate place. They call it a ‘colony’ and it is commonly understood to be land outside the village. However, all the resources such as electricity, water, anganwadis are available only inside the village.
If you want to stop caste-based practices, you cannot work with the excluded people alone. Other related stakeholders have to be held accountable. Like they say in the gender discourse – if you want to end sexual violence, you have to get the male members of the community involved.
3. Political rehabilitation
Being political is not about party politics. It is about the power of representation. If women from excluded communities want to be part of the local panchayat, they should have the space to do so. The problem is, that today, they don’t have this space.
For example, we started a campaign with rape survivors, that they should contest elections for the panchayat. As a result of this campaign, 104 women participated in panchayat elections. Almost 50 percent of them won. Many of them contested on unreserved seats. They fought and they won. The idea was for them to challenge the power structure.
Also read: The Subaltern Speaks: Marginalised Communities Will Frame Their Narratives
In some places we had to work with their family members as well, in some with the society at large. When these excluded women gain power, then at some level, the discrimination stops.
It takes years to break social barriers, even among the marginalised
Jan Sahas works with manual scavengers, rape survivors and young girls who have been forced into commercial sexual exploitation. One of the biggest challenges we face is that it is very difficult to make these communities come together. Getting ‘outsiders’ to change their social behaviour requires work at a different level. But even within these disadvantaged groups, people follow discrimination and untouchability practices.
For example, in Bhaurasa, a village in Madhya Pradesh, we had women who had managed to stop doing caste-based work. There were 17 women from the Valmiki community, and 10 from the Hela community. Valmiki is a Dalit Hindu community, while Hela is a Muslim community. It took us three years to bring them together in one place for a meeting.
For two and a half years, we conducted meetings with adults in the community to convince them. Despite that we failed to change their beliefs. But when we started working with the young – using games and activities – it took almost no time.
The current strategies which are made by the government or other institutions, rarely involve the affected communities.
One of the games we played was taking one child from the Valmiki community and the other from the Hela – one a Dalit and the other a non-Dalit. We told them that the Dalit child would become non-Dalit for a day, and vice versa.
We observed a big change in behaviour. The children soon realised that what one was doing with another human being was not based on any rationale. There is no rationale for caste discrimination, and that it didn’t make sense to follow this nonsensical practice.
The activities brought about a change in the children; they then started convincing their families and the families changed because of the children’s intervention.
Communities can solve their own problems. All they need are platforms.
Most of us in civil society who work with marginalised communities feel that ‘we are going to give them something’, ‘deliver’ something. In reality, though, no one really is in a position to deliver anything to the community. What do we really know about the communities? How can we assume leadership on their behalf when we don’t know enough?
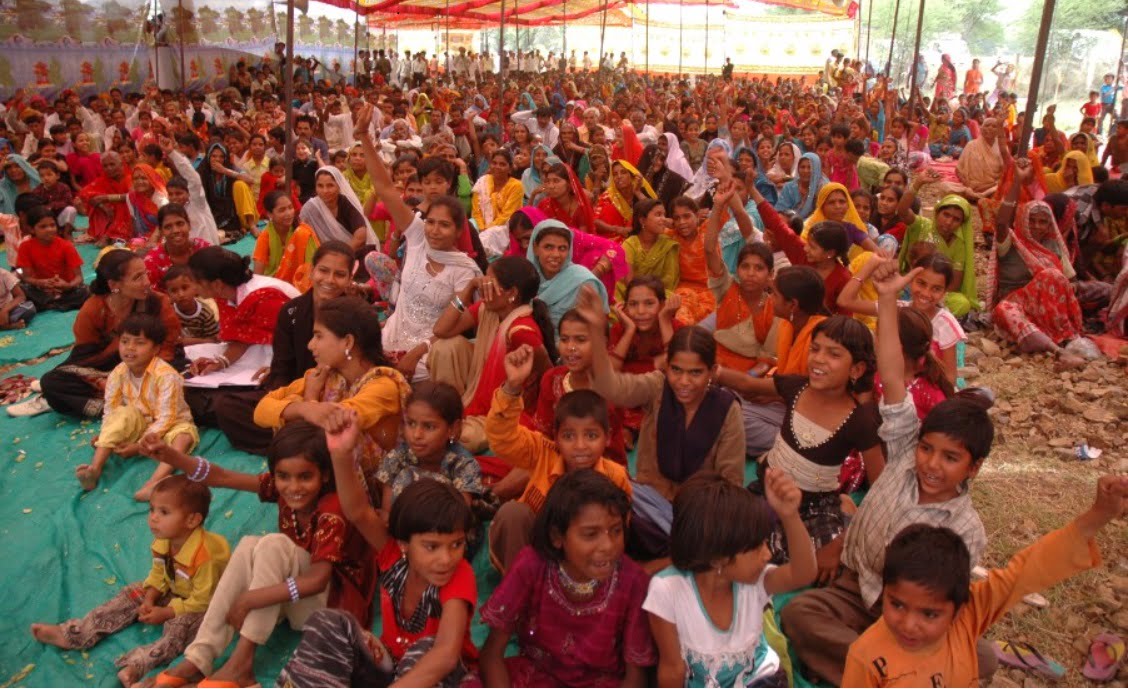
Consider the Dignity March where 25,000 rape survivors travelled over 10,000 kms and spoke openly in public forums about being raped. Jan Sahas might have coordinated the march, but the idea was not ours.
We were conducting a meeting in a village. There were four rape survivors along with their family members. One of the women said that there had been a conviction in her case, while a second women said that she was still struggling with her case and was facing many problems. The families were fighting among themselves, and demanding answers from us, saying if one woman’s case was solved, why wasn’t there a judgement yet in the second case?
One of the rape survivors told us: “You don’t explain what the problems are; let the woman who got the conviction explain to the others what steps need to be taken and how they can bring their own case to a closure”.
When she started explaining, the idea clicked in our minds; that instead of us doing this work – going to each village and talking to all the families about how to fight their cases – what if 1,000 rape survivors came together in one place and travelled all over the country and explained how to get a conviction to other survivors.
Nonprofits should only play the role of facilitators
We can’t be leaders of the manual scavengers, or rape survivors, or communities who are involved caste-based commercial sexual exploitation. They are their own leaders because they know what that pain has meant in how they live their lives. We cannot even imagine how much power or courage is required to change this situation.
No one else can do it – no Chief Minister or Prime Minister can work on it as effectively as a rape survivor can work on rape, or manual scavengers can work on their own issues. We need to understand this.
Also read: How Inclusive Is India’s ‘Development’ Of Adivasi Communities?
The role of the government or nonprofits is limited in this. We can help create appropriate forums for them; but it is they who will come up with the strategies. During the march, we observed this very clearly: people who’ve been facing oppression and discrimination, were ready to take up the struggle; they were ready to find solutions. What they needed was a platform to talk about their issues.
The current strategies which are made by the government or other institutions, rarely involve the affected communities. But no external force can bring about real change in society. Only the community itself can.
Ashif Shaikh is an Indian social activist, known for his role in Rashtriya Garima Abhiyan, a campaign for the eradication of manual scavenging. He is also a co-founder of Jan Sahas, a human rights organisation.
This article was originally published on India Development Review and has been re-published here with permission.
Translations from Hindi to English by Anupamaa Joshi.
Featured Image Credits: Jan Sahas
About the author(s)
India Development Review (IDR) is India's first independent online media and knowledge platform for the development community.