By Satish Malviya
“Had I been at work, I would not have let this happen,” regrets Sharda Kushwaha (29), an Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHA) from Neh Pipariya village in Vidisha district, Madhya Pradesh.
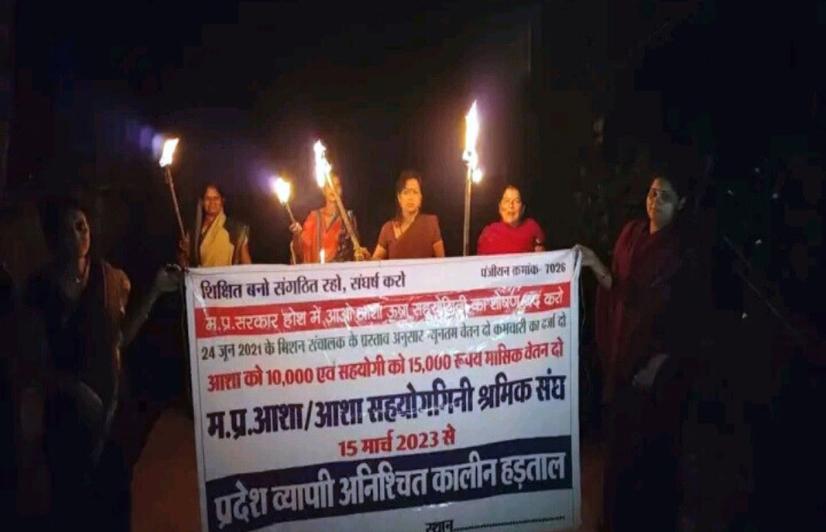
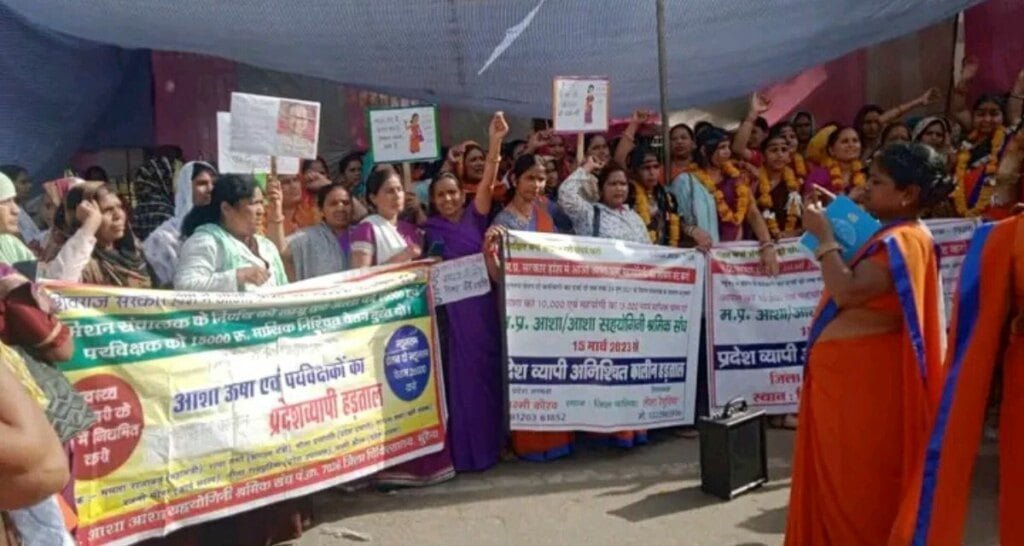
On April 13, a village woman lost her newborn shortly after delivery as the child was in breech position (bottom down and head up) in the womb. The family could not figure out that something was amiss and couldn’t seek timely medical intervention. All this, as Sharda and thousands of ASHAs have been on an indefinite strike in Madhya Pradesh since March 23, demanding that they be given a fair increase in their monthly stipend and assured of permanent employee status.
ASHA supervisor Vinita Sharma claims three women and four newborns died in Vidisha district ever since the strike — a reminder of how rural health services rely heavily on the ASHAs in their role as providers of crucial outreach services under the Reproductive, Maternal, Neonatal, and Child Health and Nutrition (RMNCHN) strategy of the National Health Mission.
“Ever since the strike began, non-institutional deliveries are on the rise. If we take the last one-month period, seven deliveries have taken place at homes in my block. I feel this number would have otherwise been zero as the pregnant women would have been shifted to a hospital or health centre,” says Preeti Raghuvanshi, an ASHA supervisor from Tyonda block of Vidisha.
“Pregnant women go to the government hospital only because of the ASHAs. In fact, no one wants to go there without an ASHA’s escort. They think there is a lack of resources in government hospitals, and that people will not provide the required information or behave well. So women do not want to go to the hospital alone,” Lakshmi Korav, the president of Madhya Pradesh ASHA/ASHA Sahyogini Shramik Sangh, tells 101Reporters.
Admitting that non-institutional deliveries have gone up ever since the strike, Korav says, “Even check-ups and monitoring of pregnant women have stopped. The ASHAs used to get them medicines from health centres or check their blood pressure during door-to-door surveys. After delivery, they are encouraged to breastfeed. The ASHAs take care of the newborn in the first 28 days and constantly monitor their weight. All of this has stopped.”

Nargis Bi of Sirnota is pregnant, but she will have to go alone to the primary health centre (PHC) for check-up. “The ASHA always accompanied me for check-ups. Everything went well when she was around. Sometimes, she would take me to the district hospital for an ultrasound. She can better articulate my problems to the doctor, which makes treatment easier.“
For now, the ASHAs have been instructed to verbally keep in touch with the women and explain what they should necessarily do. “These are the people of our community; we have no enmity towards them. We care about the people we look after. We have told them that right now we are on strike and cannot come to take care of your child. It bothers us that we cannot help them while we are fighting for our rights,” says Korav.
Why strike work?
There are three working cadres — ASHA, Urban Social Health Activist (USHA), and ASHA Sahyogini. Currently, the ASHAs and USHAs receive a monthly payment of Rs 2,000, while ASHA Sahyoginis, who perform supervisory duties, get Rs 10,000. They want the honorarium to be raised to a minimum of Rs 18,000 and Rs 26,000, respectively.
“After working tirelessly for hours together, we are paid less than a daily wage worker. My family has seven members. Tell me how I will run the household with this meagre amount,” asks Sharda. Korav emphasises that they are only demanding a living wage. “We need at least Rs 18,000 per month, which is the minimum wage a trained worker in Madhya Pradesh should get as per the government mandate.”
However, the current focused demand relates to an agreement reached during talks with a government delegation headed by Chhavi Bhardwaj, the then NHM Mission Director, in 2021. “On June 24, 2021, when we were protesting in Bhopal, the government team engaged in talks with us, and it was agreed upon that the ASHAs would be given Rs 10,000 per month and Sahyoginis Rs 15,000. We seek the immediate implementation of this agreement and payment of arrears from that date,” Korav explains.
NHM State Director Priyanka Das did not respond to repeated attempts to contact her.
Justifying the demand for a better honorarium, Sharda says they are on call 24×7. “We leave everything to tend to a woman in labour in the middle of the night, yet join routine work early morning the very next day.”
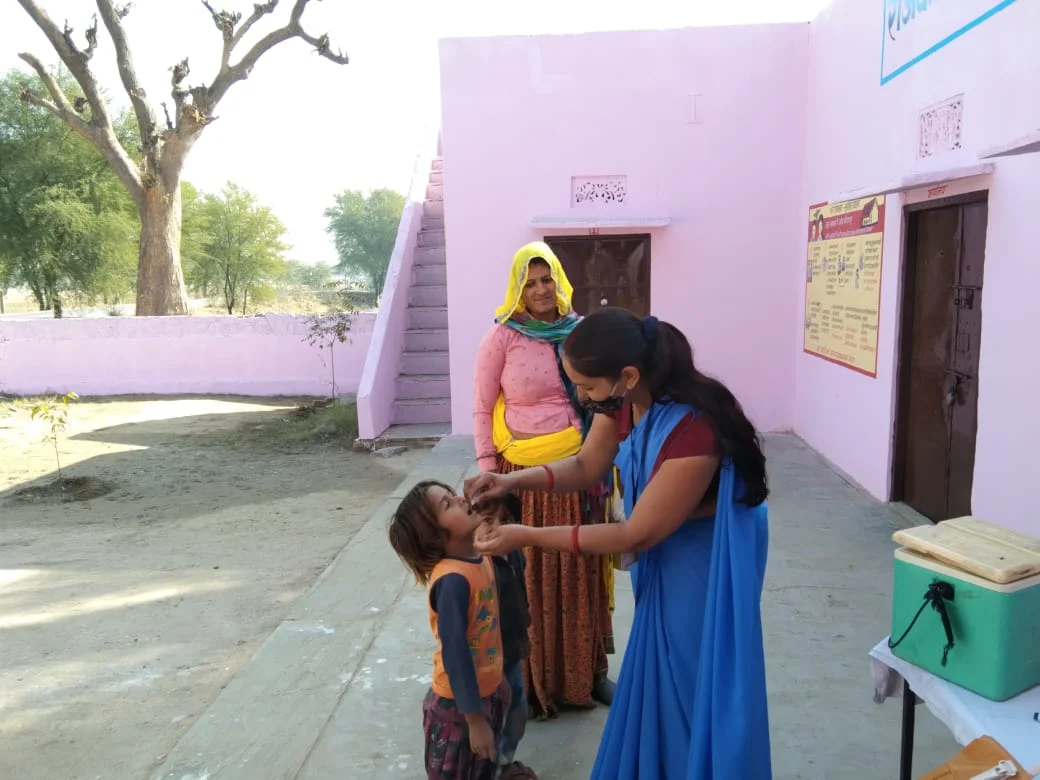
The ASHAs maintain a register of pregnant women, newborns and other target beneficiaries. Every day, they go through a checklist and mark the areas that need home visits — like pregnant women in the last trimester or breastfeeding mothers — and set out on foot for door-to-door visits as soon as they are done with the work at the PHC. These visits facilitate early detection of diseases, maternal and child healthcare, nutrition education and immunisation campaigns.
The ASHAs are like an extended family, intimately involved in the lives of the villagers they serve. They not only provide essential healthcare but also act as sources of support. “Being part of the local culture and customs makes it easier to tackle sensitive health topics. We counsel the residents on numerous issues. We talk about family planning and encourage sterilisation… We know which house has what issue, and how it should be addressed,” says Usha Sharma, an ASHA from Sirnota.

Pooja Kushwaha from Ahmedpur is forever thankful to the ASHA who supported her during pregnancy. “I was underweight, had low BP and suffered from bouts of nervousness… Arti Lodhi, our ASHA, checked upon me regularly, and sometimes accompanied me to the PHC for check-up. She gave me iron tablets. After her counselling session, I was no longer anxious about the delivery,” says Kushwaha, who also got maternity assistance under the Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY) with her help.
The JSY is a centrally sponsored scheme that integrates cash assistance with delivery and post-delivery care. The scheme has recognised ASHAs as an effective link between the government and pregnant women. It aims at promoting institutional deliveries and reducing maternal and neonatal mortality by providing cash incentives to those who give birth in healthcare institutions.
“She (ASHA) has been with us from the beginning of pregnancy. She advised me about both maternal and child health. After the baby’s arrival, she only took care of the vaccination, weight, nutrition and everything else,” attests Sunaina Bairagi, a new mother from Ahmedpur.
The ASHAs hold weekly sessions with the women and children at anganwadis to ensure holistic development and well-being of children, pregnant women, and lactating mothers. “We are trained in providing assistance during childbirth in both home and institutional settings. No one knows exactly when a delivery will happen, so we are always prepared when a woman is expecting,” says Usha.
They also maintain a record of the children’s growth and development. “Ever since the strike, the data on nourishment levels of children have not been shared with the government. No one is tracking nutritional intake. These children are walking a fine line between undernourishment and malnourishment,” cautions Korav.
The ASHAs were to start the registration work for the newly-launched Madhya Pradesh Mukhyamantri Ladli Behna Scheme, but they have not been part of it due to the strike. The referral system has been affected as the ASHAs play a critical role in facilitating timely and appropriate referrals for emergency obstetric care.
Around March-April, they conduct a malaria survey to check the presence of mosquito larvae on household premises. Vaccination drive against Japanese Encephalitis is also carried out during this period. None of these activities have been taken up this time.
No doubt, the ASHA strike has crippled rural health services in Madhya Pradesh. The only thing left to know is how long the government will take to intervene.
Satish Malviya is a Vidisha-based freelance journalist and a member of 101Reporters, a pan-India network of grassroots reporters.
About the author(s)
101Reporters is a pan-India network of grassroots reporters that brings out unheard stories from the hinterland.